Figure 3.
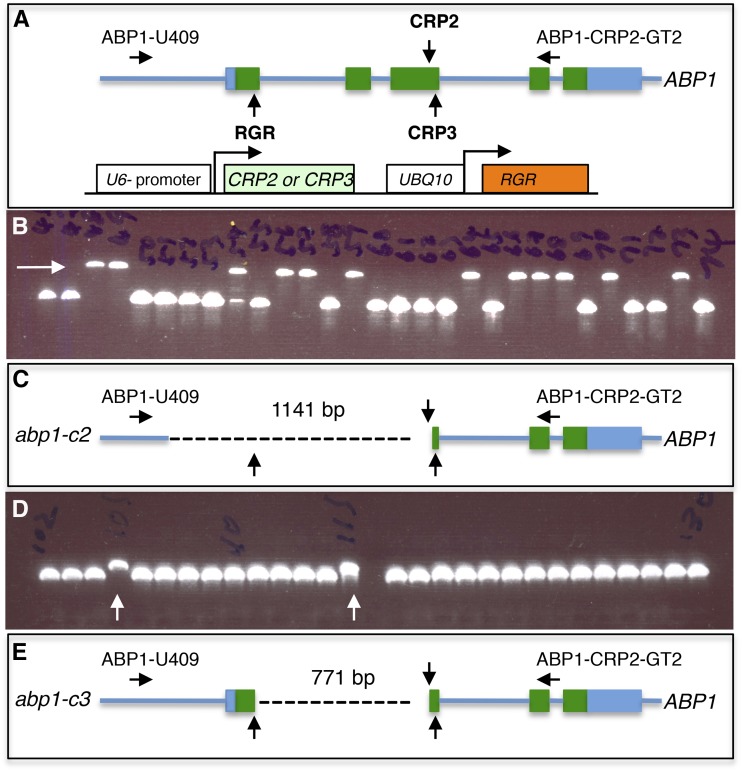
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletions of a large DNA fragment between two gRNA target sites in Arabidopsis. A, We produced CRISPR plasmids that target three sites of the ABP1 gene. We combined the RGR and CRP2 modules to delete the first three exons. We also combined the RGR and CRP3 modules in another plasmid. RGR is controlled by the UBQ10 promoter. Green boxes refer to ABP1 exons. Vertical arrows point to gRNA target sites. ABP1-U409 and ABP1-CRP2-GT2 are the primer pair used in the PCR screening. The RGR sequence and design are shown in Supplemental Figure S2. B, PCR amplification using ABP1-U409 and ABP1-CRP2-GT2 primers and the genomic DNA from Cas9-free T2 plants generated from a single T1 plant transformed with the RGR-CRP2 dual gRNA vector. About half of the plants contained a deletion. Note that this primer pair preferentially amplifies the small fragment and cannot differentiate homozygous from heterozygous plants. C, Schematic representation of the abp1-c2 mutation, which is a deletion of 1,141 bp including the first three exons and 304 bp of the ABP1 promoter. The dashed line represents the deleted region. D, Identification of a second abp1 allele that has a large deletion. Only two plants (105 and 115) out of 96 Cas9-free T2 plants from a single RGR-CRP2 T1 plant contained a deletion (arrows). E, Further sequencing analysis shows that the deletion is 711 bp, which is the exact expected size generated by gRNAs targeting RGR and CRP2 sites.