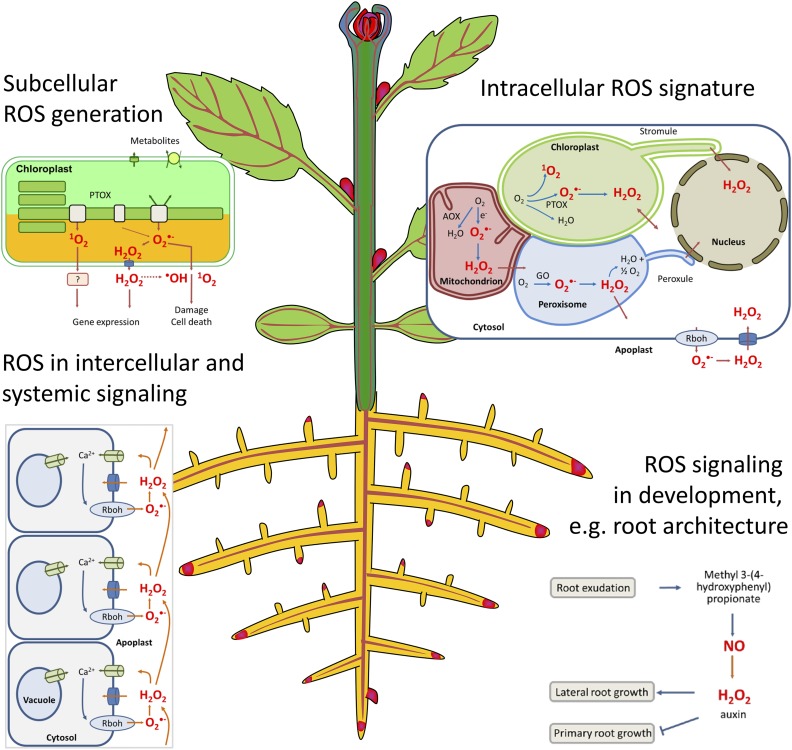
Figure 1.
Some of the multiple regulatory roles of ROS in plants addressed in this Focus Issue. Subcellular sites of ROS generation, e.g. in the chloroplast or mitochondrion, determine processes such as gene expression, cellular damage, and cell death. Progress has been made in understanding intracellular ROS transfer; formation of protrusions such as stromules, peroxules, and matrixules; and the ROS network of cells. ROS play a profound role in intercellular and long-distance communication in plants. In addition to their roles in environmental acclimation, ROS are receiving increasing awareness for their function in developmental processes such as the regulation of root architecture, polar growth, and organ senescence. Abbreviations not defined in the text: AOX, alternative oxidase; GO, glycolate oxidase; PTOX, plastid terminal oxidase.