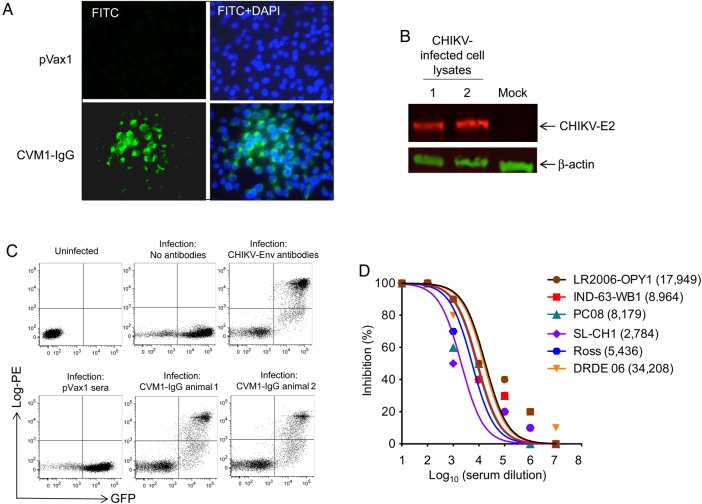
Figure 2.
Binding analyses and neutralization activity of CVM1–immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies. A, An immunofluorescence assay demonstrated that IgG generated from CVM1-IgG–administered mice was capable of binding to chikungunya virus (CHIKV) envelope protein (Env). CHIKV-infected Vero cells were fixed 24 hours after infection and evaluated by an immunofluorescence assay to detect CHIKV Env antigen expression (green). Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Sera from control mice injected with pVax1 were used as a negative control. B, The binding affinity of sera from CVM1-IgG–injected mice (day 15) to target proteins was tested by Western blot, using cell lysates from CHIKV- or mock-infected cells as described in “Materials and Methods” section. Protein transferred membranes were reprobed with antibody against β-actin was used as a loading control. The image presented here was cropped from an original image and is representative of several gels. C, Fluorescence-activated cell-sorting analysis of the binding of sera from plasmid-injected mice to CHIKV-infected cells. The x-axis indicates green fluorescent protein (GFP) staining, using the lentiviral GFP pseudovirus complemented with CHIKV Env. The y-axis demonstrates staining of infected cells by human IgG produced in mice 15 days after injection with CVM1-IgG. Staining with a control anti-CHIKV antibody (Env antibody) is also shown, as well as staining with no antibodies and pVax1. The presence and number of double-positive cells indicate presence and level of sera binding to the CHIKV-infected cells. D, Sera from mice injected with CVM1-IgG via electroporation possess neutralizing activity against multiple CHIKV strains (ie, Ross, LR2006-OPY1, IND-63-WB1, PC-08, DRDE-06, and SL-CH1). Neutralizing antibody titers are plotted, and 50% inhibitory concentrations (IC50 values; parenthesis) were calculated with Prism GraphPad software. Similar results were observed in 2 independent experiments with at least 10 mice per group for each experiment.