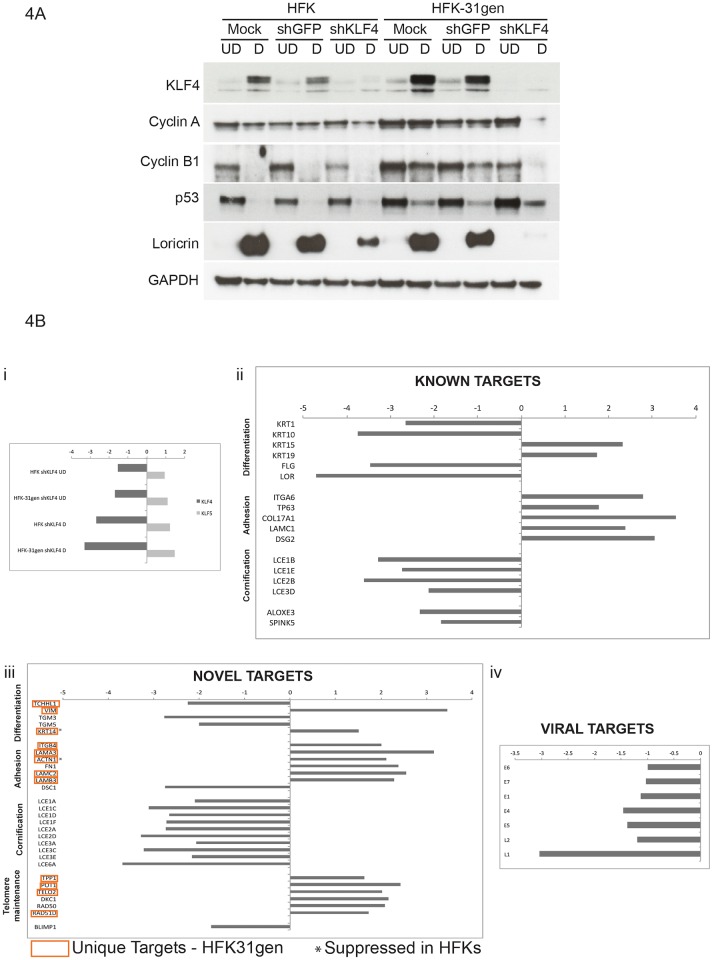
Fig 4. KLF4 regulates a distinct set of cellular targets between HPV-31 and normal keratinocytes.
(4A). Genetically matched sets of HFK and HFK-31gen cells were transiently silenced for KLF4 using lentiviral transduction and were subsequently analyzed for known cellular targets of KLF4 using western blot analysis. KLF4 silencing was comparable between the two cell types as represented in the top panel. Silencing KLF4 in HFK-31gen cells had significant reductions in the levels of cyclin A, cyclin B1 and loricrin and an increase in p53 levels. In contrast, these changes were not observed in HFKs as evident from comparable levels of cyclin A, cyclin B1 and p53 between control and KLF4 silenced HFKs. Loricrin levels were modestly reduced by KLF4 silencing in HFKs as compared to HFK-31gen cells, where a complete loss of expression was detected. GAPDH served as a loading control. (4B). RNA isolated from the same cells as in (4A) was subjected to RNA-seq analysis. (i) KLF4 knock down was confirmed and was comparable between HFKs and HFK-31gen samples in both undifferentiated and differentiated conditions. Levels of related KLF5 did not vary upon KLF4 silencing. (ii, iii) Differentially expressed targets are represented as fold differences upon KLF4 silencing in differentiated HFK-31gen cells over HFKs. These differentially expressed targets were categorized into known and novel KLF4 targets. Targets under known and novel categories were further separated based on their known biological functions. (iii) Targets specifically regulated only in HPV-positive HFK-31gen cells, while unchanged in HFKs are marked with red boxes. Targets such as KRT14, and ACTN1 were suppressed in HFKs but activated in HPV-positive cells and are highlighted with asterisks. (iv) Viral targets of KLF4 are represented as fold reduction upon KLF4 silencing in HFK-31gen cells compared to shGFP controls.