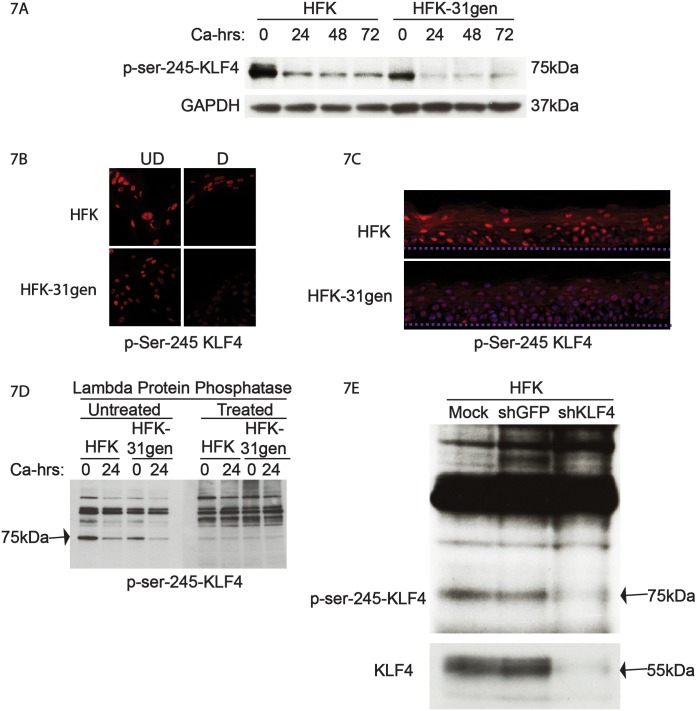
Fig 7. KLF4 is hypo-phosphorylated in HFK-31gen cells compared to HFKs.
(7A). Genetically matched HFKs and HFK-31gen cells were grown in high calcium media to induce differentiation and protein levels of phospho-ser-245 KLF4 were analyzed by western blot analysis. Levels of p-ser-245 KLF4 were lower in HKF-31gen cells than HFKs in both undifferentiated (0 calcium) condition and differentiated high calcium conditions throughout the time course. (7B). Immunofluorescence analysis for p-ser-245 KLF4 also showed a similar trend to western results, where HFK-31gen cells showed less intense staining than HFKs in both undifferentiated and differentiated conditions. (7C). HFK-31gen rafts stained less intensely for p-ser-245 than HFK rafts. (7D). Protein lysates from the analysis shown in panel A were electrophoresed in SDS polyacrylamide gels, and western blot analysis performed in duplicate. These were then treated with either mock- or protein phosphatase and then analyzed with antibodies for p-ser-245 KLF4 levels. Phosphatase treatment specifically reduced the levels of the 75kDa band confirming that it is a phospho-specific band. (7E). Protein lysates from KLF4 silenced HFKs were analyzed for KLF4 and p-ser-245 KLF4 levels. Silencing KLF4 reduced KLF4 levels (bottom panel) as well as the 75kDa p-ser-245 band confirming that it is a KLF4-specific band.