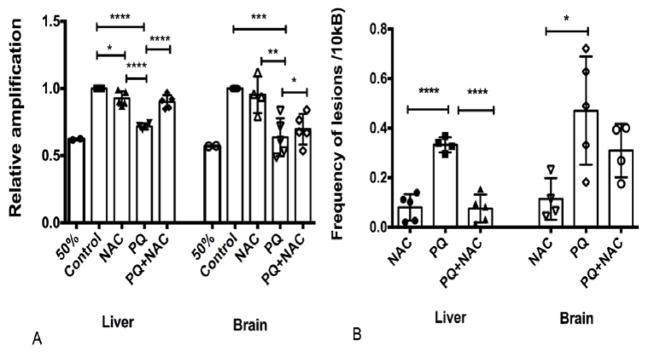
Figure 4.
Mitochondrial DNA damage (A) Relative amplification of mtDNA and (B) Poisson analysis for detection of lesions frequency in mtDNA both of liver and brain tissues of mice. Bars represent mean ±1.96 (SD) with distribution of samples per group in scatter blot column. (A) Relative amplification for liver tissue-Interval of confidence at 95% were as follow: Control: 1+/−1.96(0), NAC: 0.92 +/− 1.96 (0.10), PQ: 0.71 +/− 1.96 (0.07), and PQ+NAC: 0.90 +/− 1.96 (0.09). The sample size of the experimental groups was as follow: Control (N=5), NAC (N=5), PQ (N=4), and PQ+NAC (N=5). Relative amplification for brain tissue-Interval of confidence at 95% were as follow: Control: 1+/−1.96(0), NAC: 0.95 +/− 1.96 (0.18), PQ: 0.63 +/− 1.96 (0.16), and PQ+NAC: 0.69 +/− 1.96 (0.15). The sample size of the experimental groups was as follow: Control (N=5), NAC (N=4), PQ (N=5), and PQ+NAC (N=5). (B) Poisson analysis for liver tissue-Interval of confidence at 95% were as follow: NAC: 0.07 +/− 1.96 (0.10), PQ: 0.33 +/− 1.96 (0.08), and PQ+NAC: 0.07 +/− 1.96 (0.10). The sample size of the experimental groups was as follow: NAC (N=5), PQ (N=4), and PQ+NAC (N=5). Poisson analysis for brain tissue-Interval of confidence at 95% were as follow: NAC: 0.11 +/− 1.96 (0.14), PQ: 0.47 +/− 1.96 (0.20), and PQ+NAC: 0.30 +/− 1.96 (0.16). The sample size of the experimental groups was as follow: NAC (N=4), PQ (N=5), and PQ+NAC (N=4).