Figure 8.
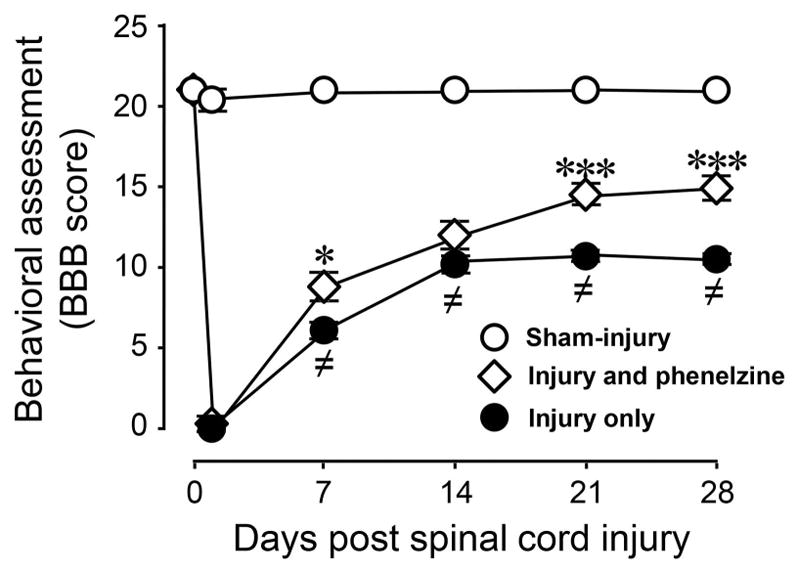
Acute systemic application of phenelzine improved locomotor function recovery after spinal cord injury. Locomotor function was assessed based on Basso, Beattie and Bresnahan (BBB) score in sham-injury, SCI only, and SCI treated with phenelzine. A significant reduction in BBB score was observed in the SCI only group compared to sham injury. Following spinal cord contusion in the SCI + phenelzine group, phenelzine (15 mg/kg) was applied daily through intraperitoneal (IP) injection for 2 weeks immediately following injury. Such treatment significantly improved the BBB score at one, three, and four weeks post-SCI, when compared to the SCI group. One-way ANOVA and Tukey test were used. (≠ P < 0.001 when compared to sham-injured; * P < 0.05 and *** P < 0.001 when compared to injury only. N = 5 in all conditions. All values were expressed as mean ± SEM.
