Figure 8.
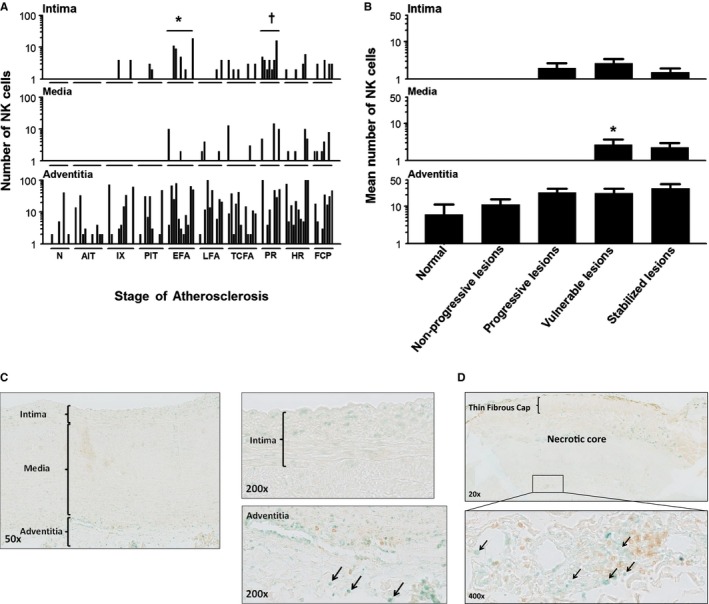
Natural killer (NK) cell (T‐bet+/CD4−) distribution during aortic atherosclerosis. A, Significantly more NK cells are seen in the intima in EFA (*P<0.01; compared to PIT) and in ruptured plaques († P<0.011; compared to TCFA). The media practically remains devoid of NK cells in progressive atherosclerosis. NK cells are constitutively and similarly present in the adventitia throughout the disease process. B, NK cells are minimally present in the aortic intima and media. NK cells are largely confined to the adventitia and the medial‐adventitial border zone, and the number of NK cells increases during the atherosclerotic process. A small, but significant, increase in NK cells in the media is seen in the vulnerable phase (viz TCFA and PR). (*P<0.001; compared to progressive lesions). Spearman's rho correlation coefficient is not significant in the intima, media, and adventitia. C, Illustrative images of a nonprogressive lesion (AIT) showing T‐Bet+/CD4– cells (methylgreen; black arrows). Note T‐helper cells (CD4+ single positive) cells in the adventitia (brown; diaminobenzidine chromogen) and the T‐helper 1 cells (CD4 and T‐bet double‐positive cells). D, Representative low‐power image of a TCFA dual immunostained for CD4/T‐bet with a high‐resolution image of the adventitia at ×20 magnification. Note the predominant adventitial location of NK cells (Vinagreen; black arrows). The lesion is a consecutive slide from the Movat and CD68 shown in Figure 3B. Total number of cases in (A and B): 100—normal 8, nonprogressive lesions 23 (viz AIT [12] and IX [11]), progressive lesions 31 (viz PIT [10], EFA [11] and LFA [10]), vulnerable lesions 20 (viz TCFA [12] and PR [8]), and stabilized lesions 18 (viz HR [10] and FCP [8]). Each solid bar in (A) represents the number of positively stained NK cells within the intima, media, and adventitia of a single lesion whereas the large solid bars in (B) represent the mean total number of NK cells within the aortic wall section per atherosclerotic phase±SEM. For abbreviations and a detailed description concerning the classification, see the Material and Methods section. All sections were developed with Vina green and diaminobenzidine (DAB) and counterstained with Mayer's hematoxylin. AIT indicates adaptive intimal thickening; EFA, early fibroatheroma; FCP, fibrotic calcified plaque; HR, healed rupture; IX, intimal xanthoma; LFA, late fibroatheroma; N, normal; PIT, pathological intimal thickening; PR, plaque rupture; TCFA, thin cap fibroatheroma.
