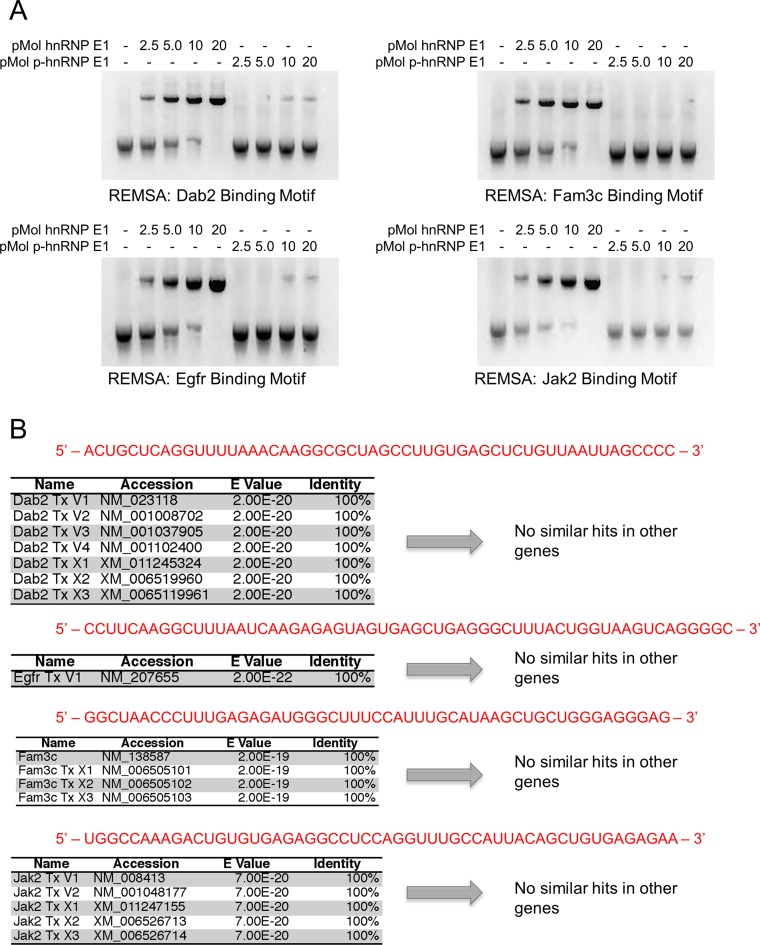
Figure 3.
hnRNP E1 binding nucleic acid motifs show a total loss of affinity for hnRNP E1 when in its phosphorylated state. (A) RNA electromobility shift assay (REMSA) analysis of synthetic regulatory motif RNA. hnRNP E1 and p-hnRNP E1 were titrated (0–20 pMol) with 1 pMol of motif RNA. RNA was labeled with [α-32P]-UTP during transcription, samples were run on non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel. The REMSA data presented are typical of three independent experiments demonstrating similar binding trends (data not shown). (B) BLASTn analysis of conserved motif results to determine uniqueness of these regulatory motifs in a genomic context. Sanger sequencing results were used as a query sequence (highlighted in red), stringency parameters were lowered to allow for the identification of patterns, rather than specific bases. Queries were performed against a mouse genomic database, containing genomic mRNA sequences.