Figure 1.
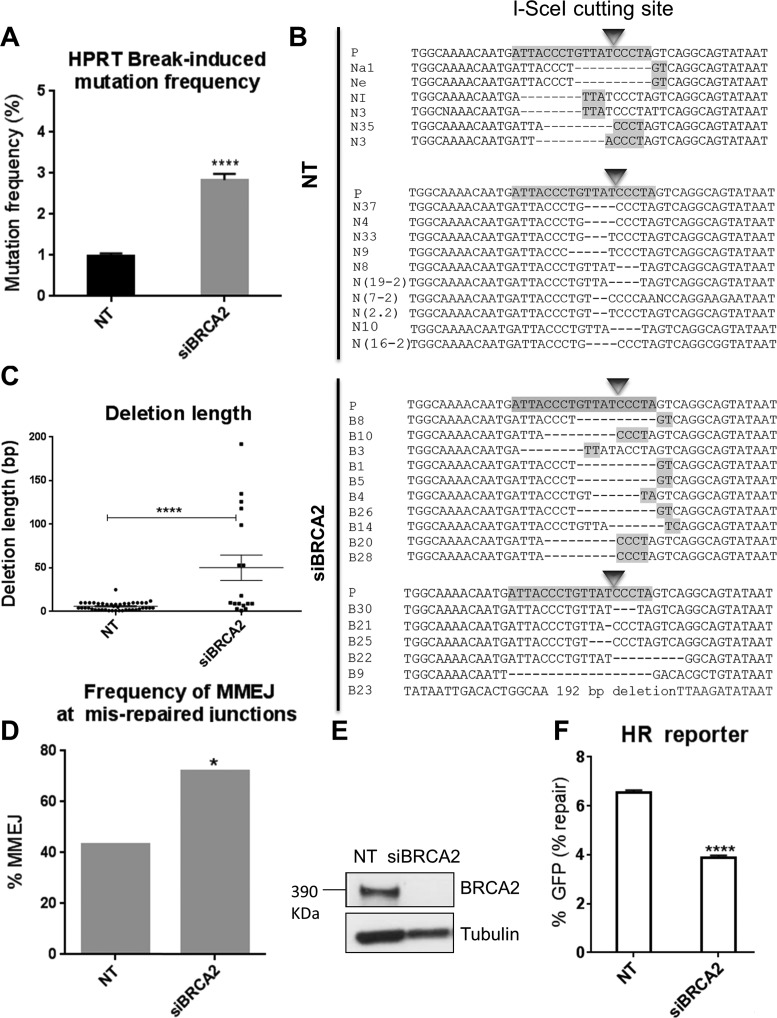
BRCA2 depletion promotes DSB-induced deletions typical of MMEJ. (A) Break-induced mutation frequency of HPRT reporter cells treated with NT control siRNA (NT), and BRCA2 siRNA (siBRCA2). Error bars represent SEM from three independent experiments. ****P < 0.0001. (B) Representative sequence alignments of the PCR products in NT control (NT), and BRCA2-depleted (siBRCA2) cells isolated from three independent experiments (see also Supplementary Figures S1A, S2A–C and S3). I-SceI recognition sequence and terminal microhomologies at the break sites are highlighted. (C) Average length of deletions (bp) in different genetic backgrounds. Each dot represents an independent clone. The lines represent mean and SEM, **** P < 0.0001. (D) Frequency of MMEJ at mis-repaired junctions in HPRT deletion mutants isolated from cells treated with NT control siRNA (NT) or BRCA2 siRNA (siBRCA2). P values calculated by statistical analysis ‘‘difference between proportions’’, * P < 0.05. (E) Western blot showing BRCA2 knockdown in HT1080 cells 48 h following siRNA transfection. (F) HR repair efficacy of DR-GFP reporter cells treated with NT control siRNA (NT), and BRCA2 siRNA (siBRCA2), indicated by the percentage of GFP-positive cells. Error bars show SEM from three independent experiments, **** P < 0.0001.