Figure 6.
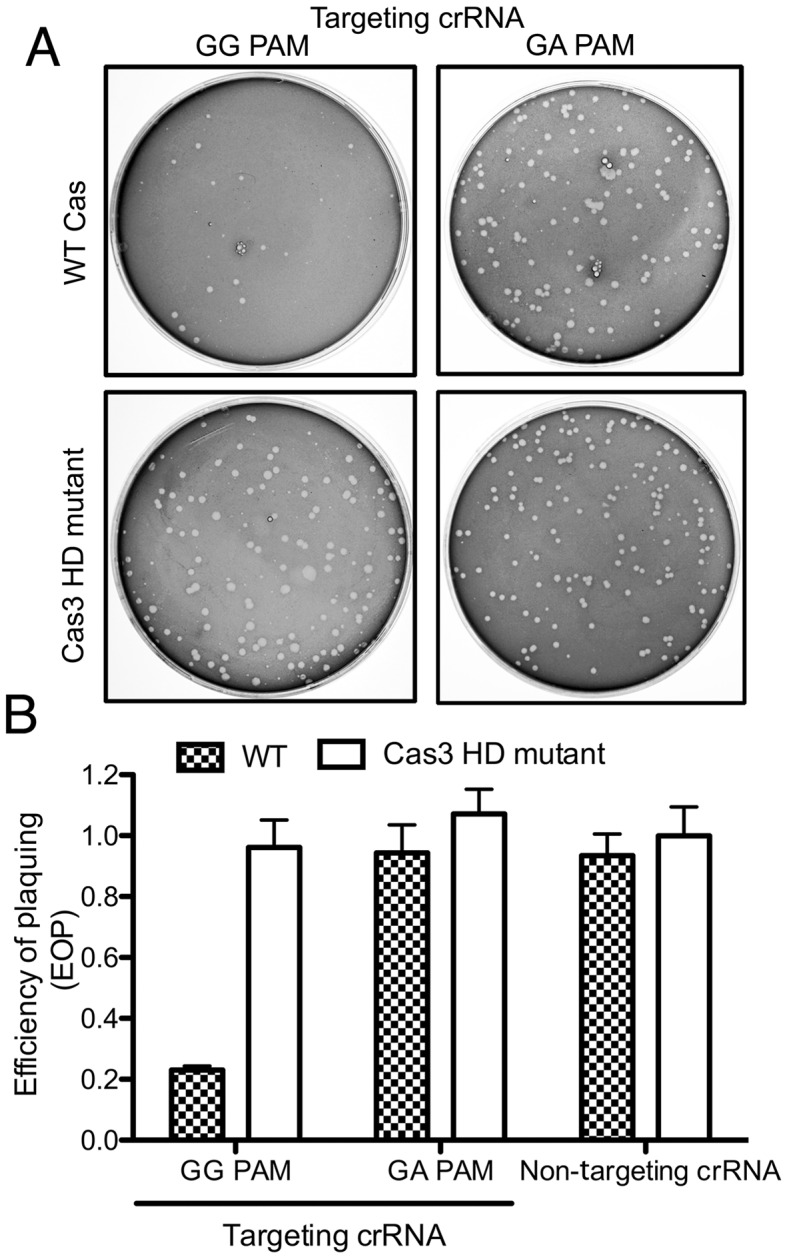
The S. putrefaciens Type I-Fv CRISPR-Cas system provides heterologous protection against lambda phage infection in E. coli. (A) Plaque formation by lambda phage was observed in E. coli BL21-AI strains carrying two plasmids: a first plasmid encoding a crRNA with a spacer of 32 nt complementarity to the lambda phage genome flanked either by a ‘GG’ or ‘GA’ PAM (targeting crRNA) and a second plasmid encoding all Cas proteins (pCas6) or pCas7 (Cas3 HD mutant). (B) Quantification of plaque formation was performed in triplicate (represented as efficiency of plaquing, EOP) of strains carrying the WT or the Cas3 HD mutant plasmid, in addition to a second plasmid producing either the targeting crRNA (in the presence of a target ‘GG’ PAM or a target ‘GA’ PAM) or a crRNA with a 32 nt non-targeting random spacer without complementarity to the phage genome. EOP is defined as the ratio between the plaque count of the strain of interest and the strain carrying empty plasmids. Bars represent mean ± SEM.
