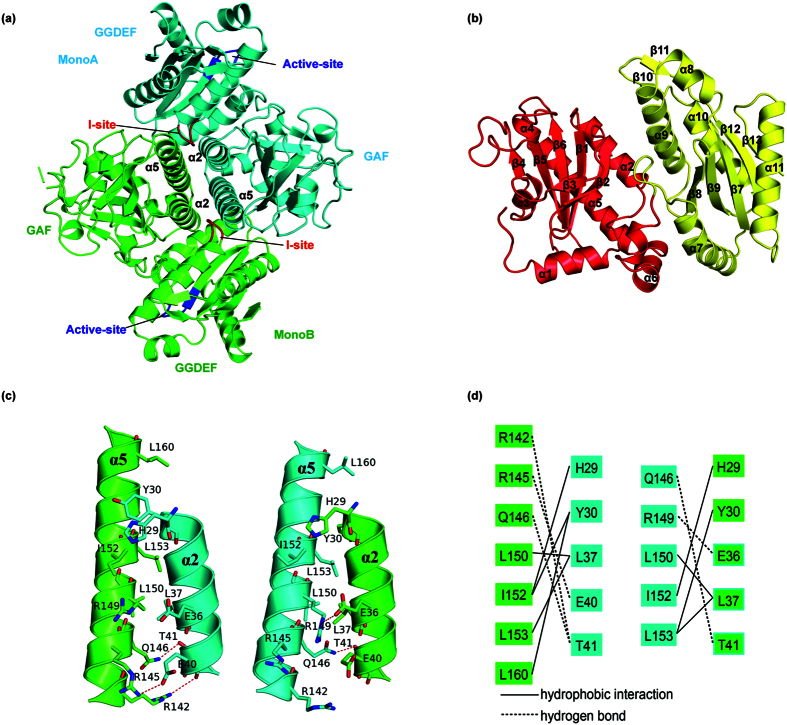
Figure 2. The structure of full-length Dcsbis.
(a) The tightly associated homodimer of Dcsbis. The A-site and I-site of Dcsbis are colored in blue and red, respectively. (b) The overall structure of the Dcsbis monomer. The N-terminal GAF domain is colored in red, while the C-terminal GGDEF domain is colored in yellow. (c,d) The hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions contributing to homodimerization.