Figure 1.
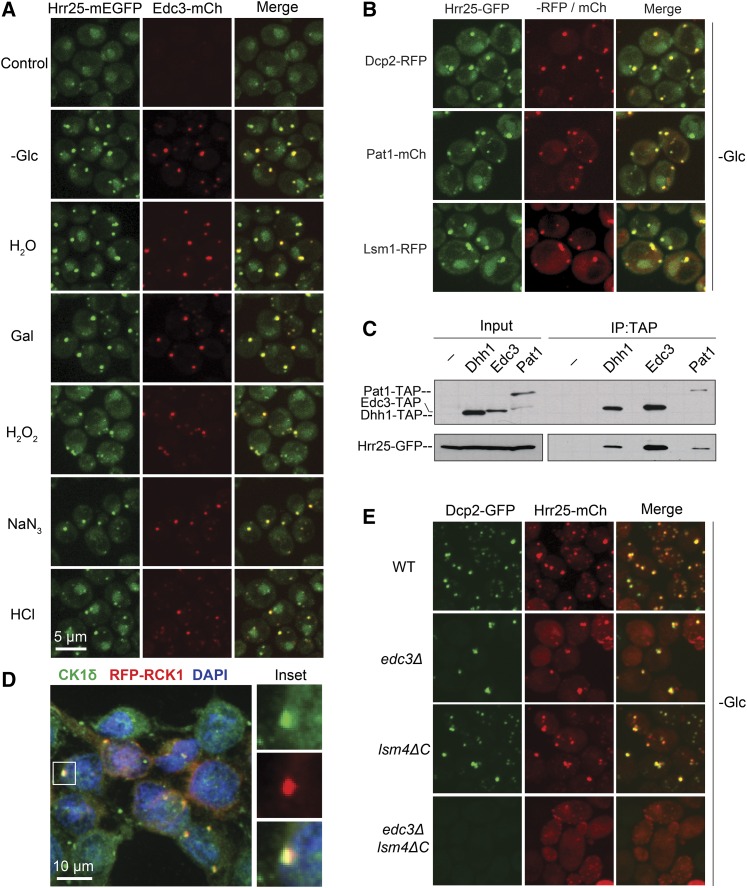
The localization of the Hrr25/CK1δ protein kinase to P-bodies is an evolutionarily conserved phenomenon. (A) Hrr25 was efficiently recruited to P-bodies in all stress conditions examined. Cells expressing Hrr25-mEGFP and Edc3-mCh were grown to midlog phase and then subjected to the indicated stress conditions. Focus formation was then assessed by confocal microscopy. (B) Hrr25 exhibited a significant level of colocalization with multiple P-body reporters. Strains expressing Hrr25-mEGFP and the indicated P-body reporters were grown to midlog phase and then transferred to a medium lacking glucose to induce P-body formation. (C) Hrr25 was detected in immunoprecipitates with multiple P-body proteins. The indicated TAP-tagged P-body proteins were precipitated from yeast cell extracts and the relative level of the associated Hrr25-GFP protein was assessed by Western blotting. (D) Human CK1δ was associated with P-bodies. P-body formation was induced in HeLa cells by the overexpression of an RCK1-RFP construct and an antibody to the CK1δ enzyme was used for immunofluorescence. RCK1 is the mammalian ortholog of the yeast Dhh1 RNA helicase (Sheth and Parker 2003; Cougot et al. 2004). The panels at the right show the CK1δ, RFP-RCK1, and merged images for the indicated focus in the main panel. (E) Hrr25 foci were absent from cells defective for P-body assembly. The localization of Dcp2-GFP and Hrr25-mCh was determined by confocal microscopy after the indicated strains had been transferred to a medium lacking glucose for 20 min. Quantitation of these data and the +Glc control images are shown in Figure S1, C and D, respectively. P-body assembly has been shown to be compromised in both the edc3Δ lsm4ΔC and pat1Δ mutants (Sheth and Parker 2003; Decker et al. 2007; Ramachandran et al. 2011).