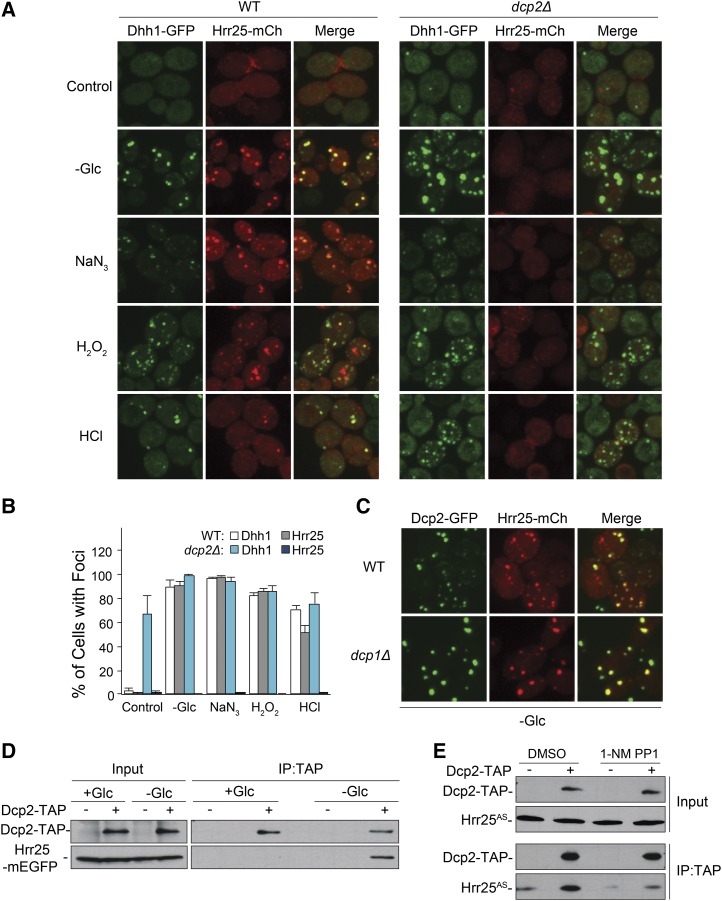
Figure 3.
The recruitment of Hrr25 to P-bodies required Dcp2, the catalytic subunit of the decapping enzyme. (A and B) The presence of Dcp2 was generally required for Hrr25 localization to P-bodies. P-bodies were induced by the indicated stress conditions in either wild-type or dcp2Δ cells. P-body foci were visualized by confocal microscopy (A) and the fraction of cells with foci were quantified (in B). (C) Hrr25 localization to P-bodies did not require Dcp1. Hrr25-mCh localization was assessed by confocal microscopy after glucose deprivation of wild-type or dcp1Δ cells. (D) Hrr25 was associated with Dcp2 specifically in glucose-deprived cells. TAP-tagged Dcp2 was precipitated from extracts prepared from either midlog phase cells (+Glc) or cells that had been starved for glucose for 30 min (−Glc). The amount of coprecipitating Hrr25-mEGFP was assessed by Western blotting with an antibody to GFP. (E) The inhibition of Hrr25 kinase activity disrupted the Hrr25-Dcp2 interaction. TAP-tagged Dcp2 was precipitated from glucose-starved cells expressing the Hrr25AS protein in the presence or absence of the drug, 1-NM PP1. The relative levels of the associated Hrr25AS protein were subsequently assessed by Western blotting.