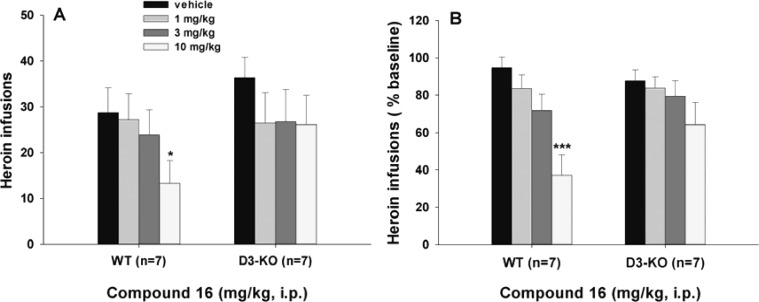
Figure 3.
Effects of compound 16 on heroin self-administration in WT and D3R-KO mice. All the data are expressed as mean ± SEM. (A) Total numbers of heroin infusions after injection of each dose of compound 16. (B) Normalized data showing drug-induced % change in heroin self-administration over new baseline immediately before each test day. One-way ANOVA with repeated measures over drug dose revealed a statistically significant drug treatment main effect in WT mice ((A) F3,18 = 2.13, p > 0.05; (B) F3,18 = 9.09, p < 0.001) but not in D3KO mice ((A) F3,18 = 0.63, p > 0.05; (B) D3KO, F3,18 = 1.78, p > 0.05). We note that one-way ANOVA did not reveal a significant treatment main effect for the data shown in (A) WT mice. However, the direct two group comparison between the vehicle and 10 mg/kg 16 groups revealed a statistically significant reduction ((A) WT, paired t test, q = 5.07, p < 0.05). These may be related to the relatively smaller group size and/or the relatively variable basal levels of heroin self-administration in different subjects. Therefore, the renormalized data (% change over baseline) are provided ((B) in this figure; the same as in Figures 2B and 4B) in this study. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, compared to vehicle.