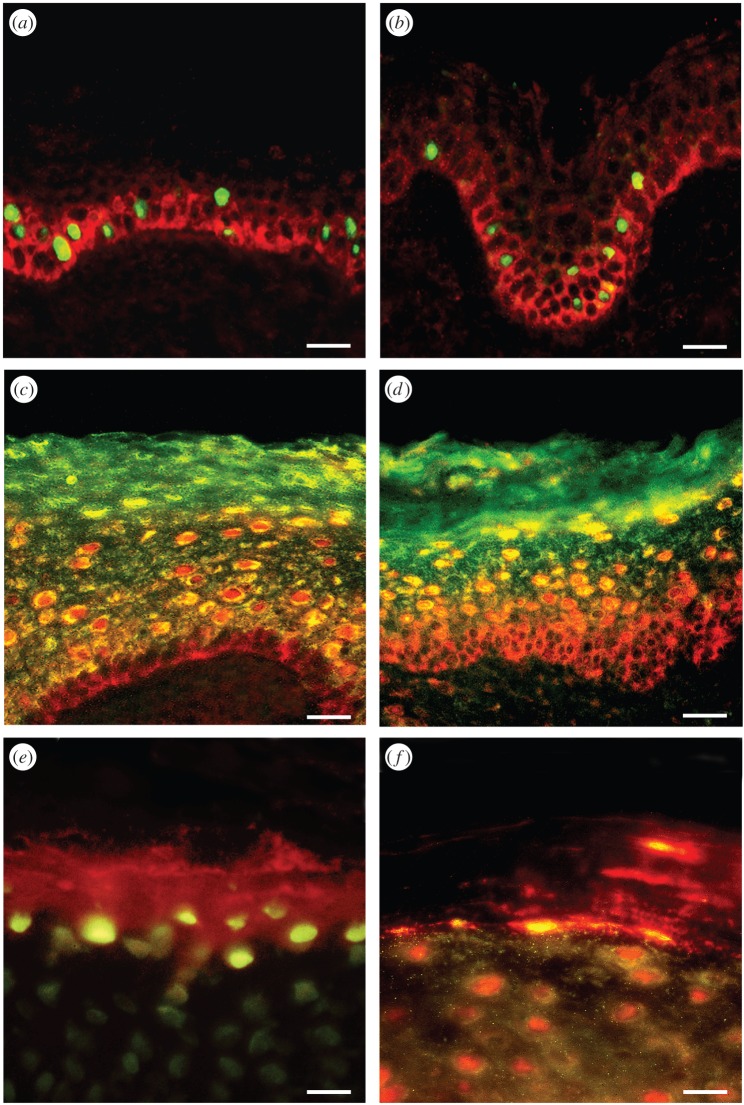
Figure 4.
Double-labelling of P2Y1 and P2Y2 receptors with markers of proliferation shows colocalization within a subpopulation of basal and parabasal keratinocytes. Double-labelling of P2X5 receptors with markers of differentiated keratinocytes shows colocalization within the stratum spinosum, and double-labelling of P2X7 receptors with markers of apoptosis in human leg skin shows colocalization within the stratum corneum. (a) Ki-67 immunolabelling (a marker for proliferation) stained the nuclei (green) of a subpopulation of keratinocytes in the basal and parabasal layers of the epidermis. P2Y1 receptor immunostaining (red) was found in the basal layer on cells also staining for Ki-67. (b) PCNA immunolabelling (a marker for proliferation) stained the nuclei (green) of a subpopulation of keratinocytes. These nuclei were often distributed in clusters and found in the basal and parabasal layers of the epidermis. P2Y2 receptor immunostaining (red) was also expressed in basal and parabasal epidermal cells. (c) P2X5 receptor immunostaining (red) showed overlap (yellow) with cytokeratin K10 (green), an early marker of keratinocyte differentiation. P2X5 receptors were present in the basal layer of the epidermis up to the midgranular layer. Cytokeratin K10 was distributed in most suprabasal keratinocytes. The stratum basale stained only for P2X5 receptors, indicating that no differentiation was taking place in these cells. The colocalization of P2X5 receptors and cytokeratin K10 appeared mainly in the cytoplasm of differentiating cells within the stratum spinosum and partly in the stratum granulosum. Note that the stratum corneum also stained for cytokeratin K10, which labelled differentiated keratinocytes, even in dying cells. (d) P2X5 receptor immunostaining (red) showed overlap (yellow) with involucrin (green). P2X5 receptors were present in the basal layer of the epidermis up to the midgranular layer. Note that the pattern of staining with involucrin was similar to that seen with cytokeratin K10, except that cells from the stratum basale up to the midstratum spinosum were not labelled with involucrin, which is a late marker of keratinocyte differentiation. (e) TUNEL (green) labelled the nuclei of cells at the uppermost level of the stratum granulosum and P2X7 antibody (red) mainly stained cell fragments within the stratum corneum. (f) Anti-caspase-3 (green) colocalized with areas of P2X7 receptor immunostaining (red) both at the junction of the stratum granulosum and within the stratum corneum. Areas of colocalization were yellow. Note that the differentiating keratinocytes in the upper stratum granulosum were also positive for anti-caspase-3. Scale bars (a–d) 30 µm and (e,f) 15 µm. (Reproduced from [88], with permission.)