Figure 2.
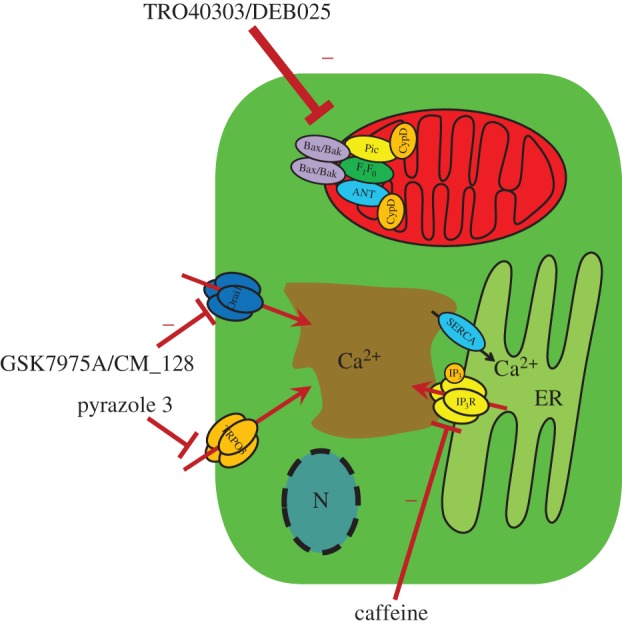
Novel therapeutic targets in AP. Experimental studies from recent years identified several proteins in cellular Ca2+ signaling machinery that might be potential target molecules in AP treatment. Caffeine and dimethylxanthines were shown to block IP3-mediated Ca2+ release from the ER that decreased the severity of AP in experimental models. Similarly, the inhibition of the plasma membrane Ca2+ influx channels Orai1 and TRPC3 reduced the severity of AP in animal models. Another treatment possibility might be the inhibition of the MPTP opening, which improved the disease outcome in rodents.
