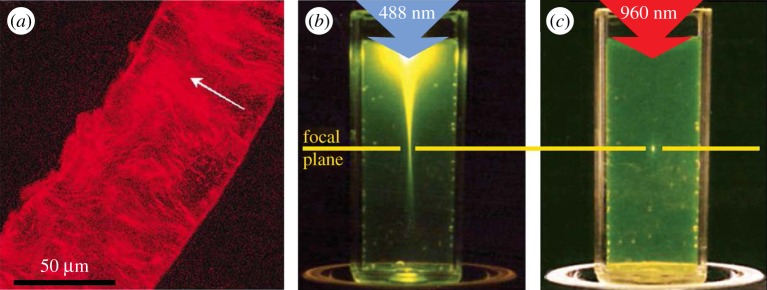
Figure 9.
Imaging bone with confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). (a) CLSM image of a single lamella from a human femur. The arrow represents a qualitative assessment of the orientation of the collagen fibrils. (Image from [63] with kind permission of Elsevier.) (b,c) Difference in the focusing capabilities of CLSM versus multi-photon microscopy. (Images from [191] with kind permission of Nature Publishing Group.) (b) In the case of CLSM, the laser beam excites molecules outside of the focal plane on its path through the tissue. (c) In multi-photon microscopy, (at least) two photons are combined to specifically excite only the molecules at the focal spot. (Online version in colour.)