FIGURE 1.
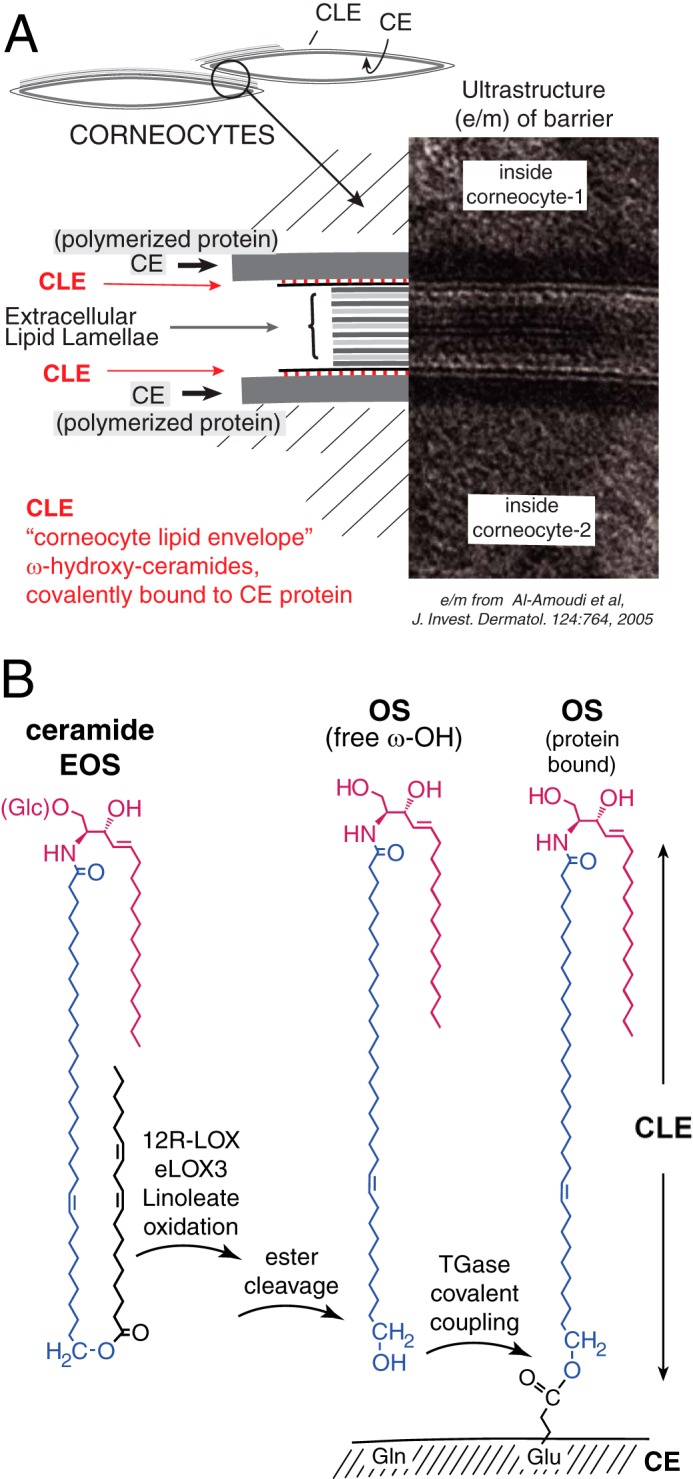
Structures of the epidermal water barrier and formation of the CLE. A, electron micrograph of the epidermal barrier with the parts illustrated in schematic style. In the barrier layer of the epidermis the corneocytes are melded together by fusion of three substructures: polymerized protein forming the corneocyte envelope (CE) on the periphery of each cell, extracellular lamellar lipids between cells, and the monolayer of covalently bound ceramides and fatty acids, the CLE, covering the corneocyte envelope and forming a scaffold for the lamellar lipids. B, our working hypothesis (8) entails LOX-catalyzed oxidation of the linoleate in EOS ceramide, facilitating hydrolysis of the ester bond, freeing OS ceramide for coupling to the corneocyte envelope protein by transglutaminase (TGase), thus forming the CLE. The electron micrograph is from Ref. 66 with permission.
