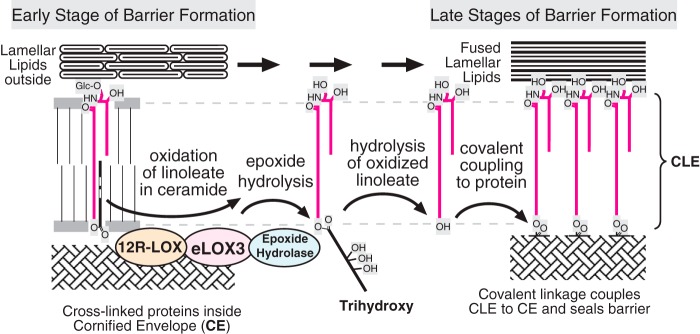
FIGURE 11.
Synthesis of linoleate triols in ceramide esters and their role in formation of the CLE. Early in barrier construction lamellar granules fuse with the corneocyte plasma membrane leaving Glc-EOS spanning the membrane (left side) (56). Ultimately, the phospholipids are cleared, being replaced by ceramides, although free OS (now de-glucosylated) is covalently coupled to the polymerized protein of the corneocyte envelope, thus forming the CLE (right side). CLE formation is facilitated by oxidation of the linoleate moiety of EOS (black chain) by 12R-LOX and eLOX3; putative epoxide hydrolase-catalyzed epoxide hydrolysis then yields esterified linoleate-triol, the polar structure of which disrupts the lipid structures and facilitates de-esterification of the EOS-type ceramides, providing the free OS for coupling to protein and thus creating the CLE.