FIGURE 3.
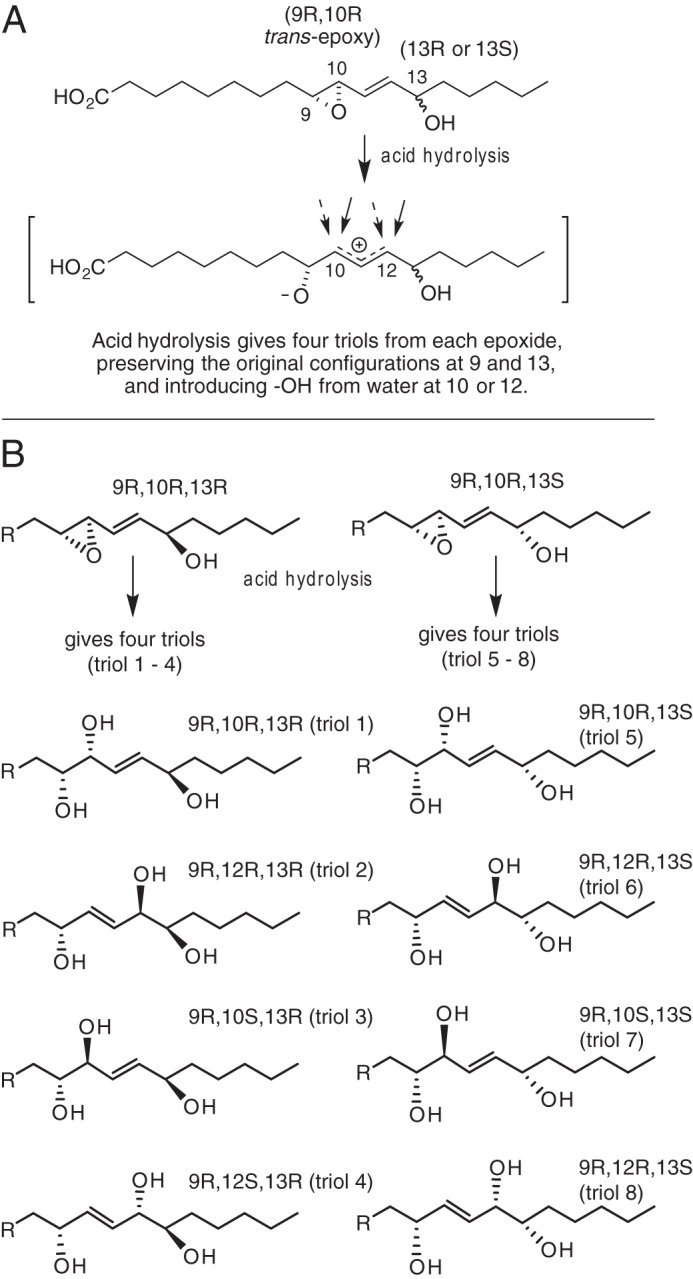
Acid hydrolysis of linoleate 9,10-epoxy-13-hydroxy epoxyalcohols and structures of the resulting triols. A, acid hydrolysis opens the epoxide ring and permits reaction of water at C-10 or C-12, producing four triol products from a single epoxyalcohol. B, left side, hydrolysis of 9R,10R-trans-epoxy-11E-13R-hydroxy-octadecenoate produces triols 1–4. Right side, hydrolysis of the diastereomer with 13S-hydroxyl produces triols 5–8. Not illustrated are the eight enantiomeric triols arising from the mirror image epoxyalcohols of 9S,10S-epoxy-13RS-hydroxy configuration. Authentic samples of triols 1–8 and the enantiomers were prepared as standards for comparison with the epidermal triols.
