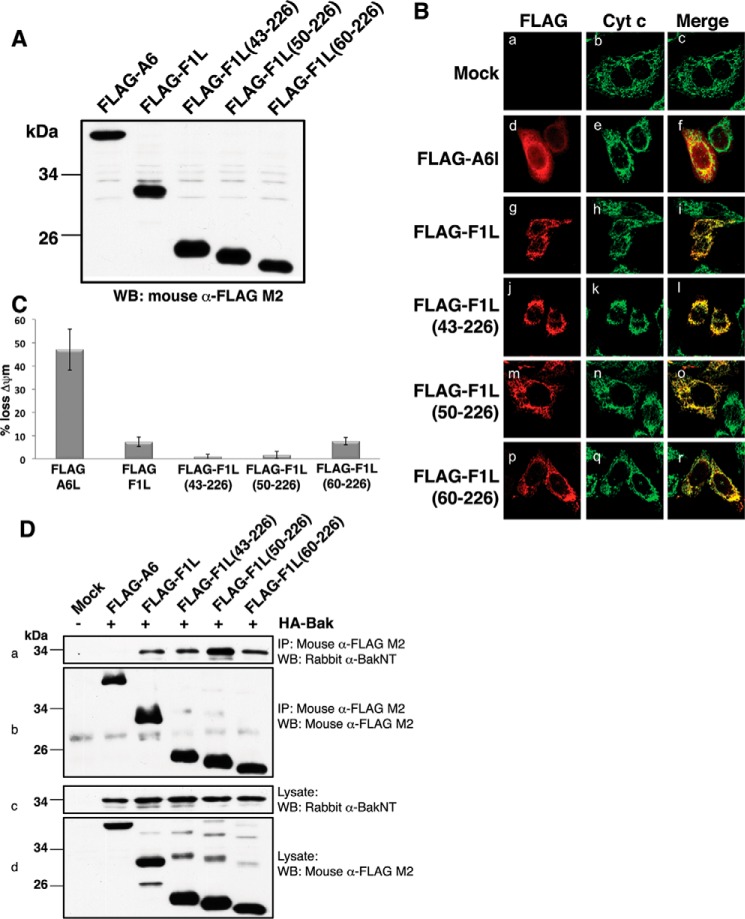
FIGURE 4.
Functional characterization of F1L truncation mutants. A, VACV(COP)F1L N-terminal truncations expression levels in HeLa cells. B, subcellular localization of VACV(COP)F1L N-terminal truncations in HeLa cells. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with empty vector (panels a–c), FLAG-F1L (panels g–i), FLAG-F1L(43–226) (panels j–l), FLAG-F1L(50–226) (panels m–o), FLAG-F1L(60–226) (panels p–r), or FLAG-A6L (panels d–f) as a control. 12 h post-transfection cells were stained with rabbit anti-FLAG M2 antibody and imaged using a Zeiss Axiovert laser scanning microscope. Mitochondria were visualized by staining for cytochrome (Cyt) c. C, VACV(COP)F1L N-terminal truncations potently protect HeLa cells against TNFα-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis was induced with 10 ng/ml TNFα combined with 5 mg/ml cycloheximide. Apoptosis was assessed by quantifying tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester fluorescence via flow cytometry, and the percentage of cells that demonstrated a loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) is given on the y axis. All experiments were performed in triplicate; error bars show S.D. D, F1L truncations efficiently immunoprecipitate Bak. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with pcDNA3-HA-BAK as well as with pcDNA3-FLAG-A6L, pcDNA3-FLAG-F1L, pcDNA3-FLAG-F1L(43–226), pcDNA3-FLAG-F1L(50–226), or pcDNA3-FLAG-F1L(60–226). FLAG-tagged F1L was immunoprecipitated with monoclonal mouse anti-FLAG M2 antibody, Bak was detected using a polyclonal rabbit anti-Bak N terminus (NT) antibody (panel a), and FLAG-F1L constructs were detected using mouse anti-FLAG M2 antibody (panel b). Panels c and d show whole cell lysates probed with polyclonal rabbit anti-Bak N terminus antibody or mouse anti-FLAG M2 antibody as loading controls, respectively. IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blotting.