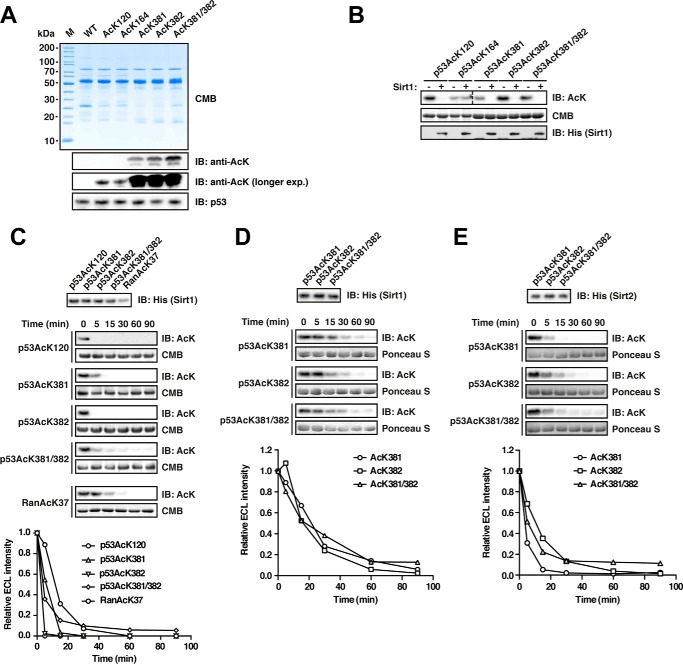
FIGURE 4.
Deacetylation of p53 by Sirt1 and Sirt2. A, p53 was site-specifically lysine-acetylated at several sites (AcK120, AcK164, AcK381, AcK382, and AcK381/382). For details on the experimental procedures, see Fig. 1A. An anti-p53 antibody was used to detect p53. B, p53 is deacetylated by Sirt1 at AcK120, AcK381, AcK382, and AcK381/382 but not AcK164 in vitro. Deacetylation assay with site-specifically lysine-acetylated p53 and Sirt1 at a molar Sirt1/p53 ratio of 1:20 (p53, 12 μm; Sirt1, 0.6 μm). The reaction was performed for 2 h at 23 °C, and the acetylation level after Sirt1-catalyzed deacetylation is determined with an anti-AcK antibody. Notably, AcK381, AcK382, and even the di-acetylated AcK381/382 were completely deacetylated under the assay conditions. Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CMB) staining was used as a loading control. An anti-His6 antibody was used to stain for Sirt1. C, time course experiment to assess Sirt1-catalyzed p53-AcK120, -AcK381, -AcK382, and -AcK381/382 deacetylation (p53, 12 μm; Sirt1, 0.6 μm). Ran AcK37 (12 μm) was used as a control. An anti-AcK antibody was used to stain for lysine acetylation, Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CMB), as a loading control. The quantification of the kinetics shown in the right panel was performed using ImageJ. Anti-His6 antibody was used to detect Sirt1. D, time course experiments as for B but with a molar p53/Sirt1 ratio of 1:200 (Sirt1, 0.06 μm) to more sensitively assess the p53-catalyzed deacetylation of p53 AcK381, AcK382, and AcK381/382. As visible in the immunoblottings and the quantifications (lower panel), both mono-acetylated p53 proteins and the di-acetylated protein show highly similar Sirt1-catalyzed deacetylation. E, Sirt2 also deacetylates p53 at AcK381, AcK382, and AcK381/382. Time course experiments were to analyze whether all three sites are also deacetylated by Sirt2 (molar ratio 1:200 as in D). All three acetylated p53 proteins were deacetylated by Sirt2 with similar rates. IB, immunoblot.