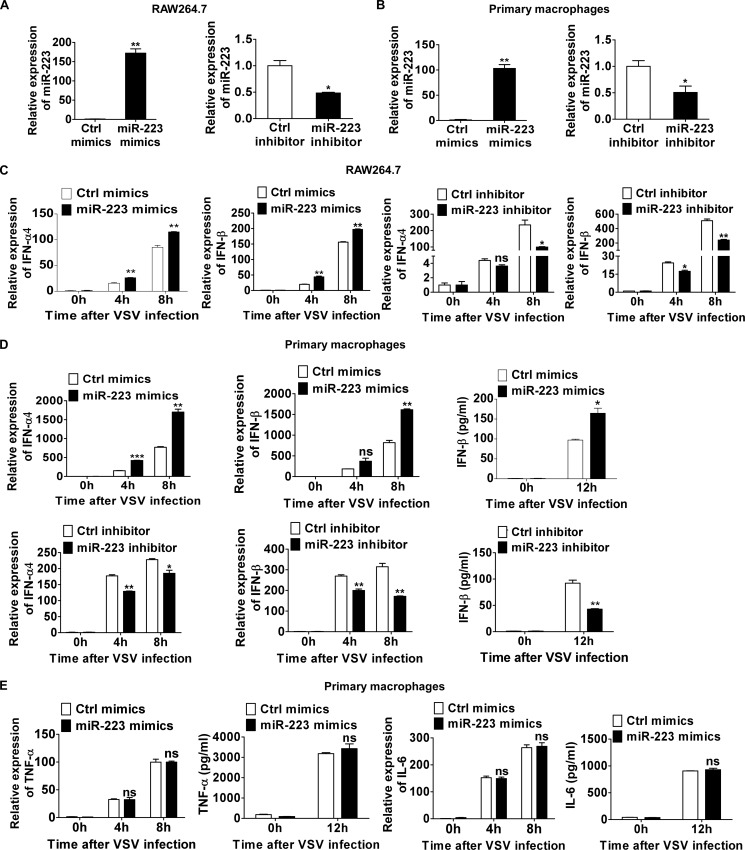
FIGURE 2.
miR-223 positively regulates VSV-triggered type I IFN production. A, 0.5 ml of 2 × 105 RAW264.7 cells were transfected with control (Ctrl) mimics or miR-223 mimics (left), control inhibitors or miR-223 inhibitors (right) as indicated at a final concentration of 20 nm. After 48 h, miR-223 expression was measured. B, 0.5 ml of 2 × 105 mouse peritoneal macrophages were transfected as described in A, and after 48 h miR-223 expression was measured. C, 0.5 ml of 2 × 105 RAW264.7 cells were transfected as described in A. After 48 h, cells were infected by VSV at m.o.i. 0.1 for indicated times. IFN-α4 (left) and IFN-β (right) mRNA expression were measured by qPCR and normalized to the expression of β-actin in each sample. D, 0.5 ml of 2 × 105 mouse peritoneal macrophages were transfected as described in A. After 48 h, cells were infected by VSV at m.o.i. 10 for indicated times. IFN-α4 and IFN-β mRNA expression were measured by qPCR. IFN-β in supernatants was measured by ELISA. E, 0.5 ml of 2 × 105 peritoneal macrophages were transfected with control mimics or miR-223. After 48 h, cells were infected by VSV at m.o.i. 10 for indicated times. TNF-α and IL-6 mRNA expressions were measured by qPCR. TNF-α and IL-6 in supernatants were measured by ELISA. Data are the mean ± S.D. (n = 3) of one representative experiment. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. ***, p < 0.1; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05; ns, not significant.