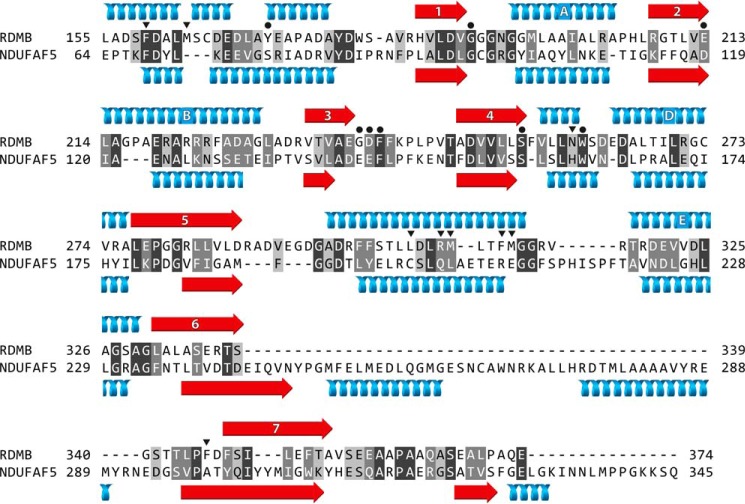
FIGURE 8.
Alignment of the C-terminal regions of the sequences of RdmB from S. purpurascens and human NDUFAF5. The N-terminal regions (not shown) are unrelated. White letters on dark gray and mid-gray indicate identical and conserved residues, respectively, and black letters on light gray are weakly conserved residues. The secondary structural elements of the 7β-strand SAM binding domain of RdmB are shown above its sequence, and the predicted secondary structure of NDUFAF5 is shown below. Helices and β-strands are blue and red, respectively. The second helix of RdmB (residues 164–167) is a 310-helix, and the others are α-helices. In RdmB, the 7β-strand methyl-transferase-fold consists of β-sheets 1–7 and intervening α-helices A–E. RdmB lacks helix C, found between β-strands 3 and 4 in some family members. The other α-helices lie outside the 7β-strand fold and contain residues involved in substrate binding. Black dots and inverted black triangles, respectively, denote amino acids involved in binding SAM, and in binding substrates and products.