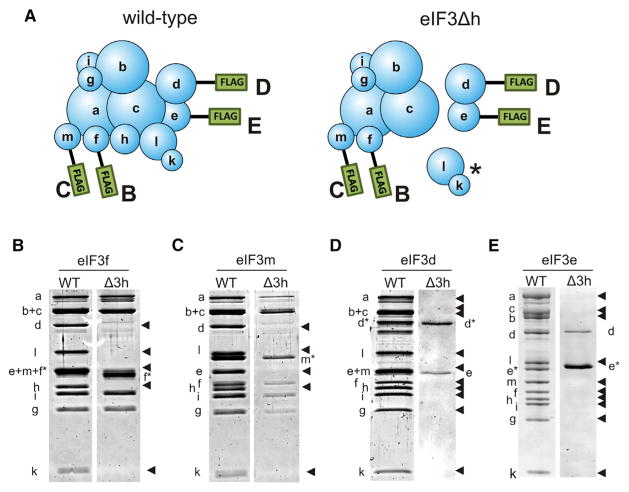
Figure 1. Deletion of eIF3h Prevents Subunits d, e, k, and l from Associating with the eIF3 Complex.
(A) Cartoons of eIF3 showing subunits tagged with N-terminal FLAG tags used for purifying eIF3 complexes from wild-type (WT) (left) or eIF3Δh (right) Neurospora mycelia. Letters beside each FLAG tag signify the gels in (B–E) that correspond with eIF3 purifications using a FLAG-tagged subunit.
(B–E) Denaturing polyacrylamide gels of eIF3 purified with FLAG-tagged (B) eIF3f, (C) eIF3m, (D) eIF3d, and (E) eIF3e. Tagged subunits are indicated over each pair of gels and to the side of the gels with an asterisk. WT or eIF3Δh genetic backgrounds are indicated over each gel. Missing subunits are indicated by arrowheads. The asterisk in (A) indicates the (k,l) subunit dimer previously shown to depend on eIF3h for assembly (Smith et al., 2013). See also Figures S1–S5.