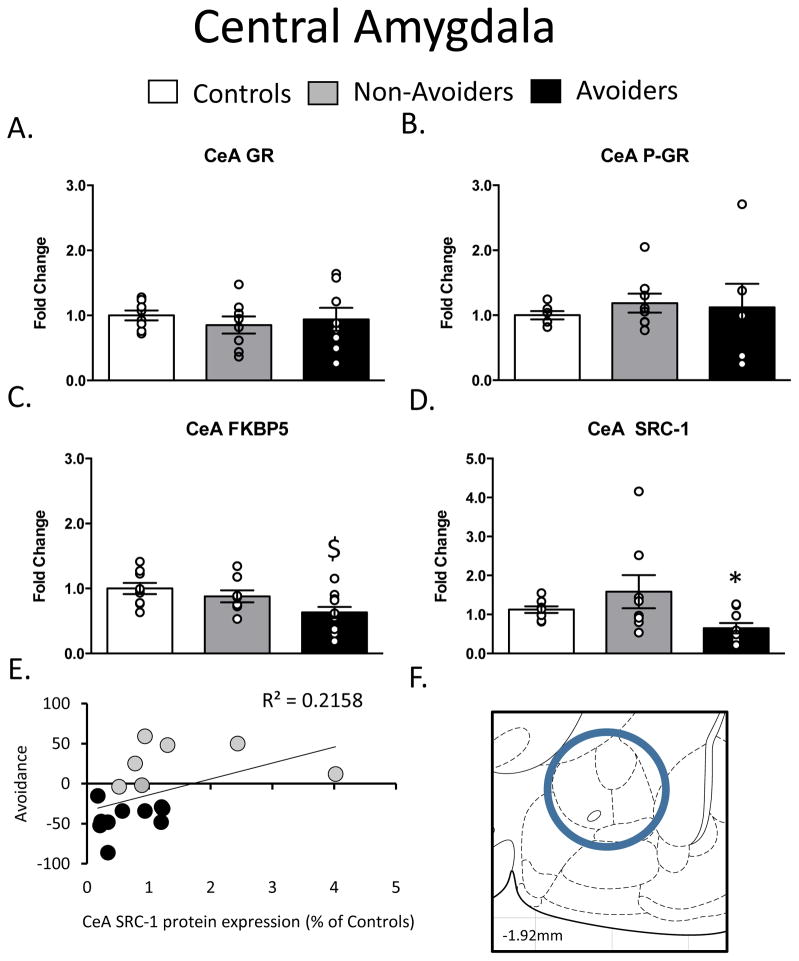
Figure 4.
Changes in Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) machinery in the Central Amygdala (CeA; AP: −1.92, ML: 4.4, DV: 8.2). A. Total GR (% of Controls), B. pGR (expressed as a ratio of pGR/GR), C. FK506 Binding Protein 51 (FKBP51) (% of Controls) and D. Steroid Receptor Co-Activator (SRC)-1 (% of Controls) measured 48 h post-odor exposure in the CeA of Controls (white bars; n=6), Non-Avoiders (grey bars; n=8) and Avoiders (black bars; n=7). E. Scatter plot for individual rats (Avoider, black dots and Non-Avoider, grey circles; Experiment 2) shows change in preference for predator-paired context versus CeA SRC-1 protein expression 48 h post-stress. Rats that exhibited high avoidance of the predator-paired context 24 h post-odor exposure had lower CeA SRC-1 expression 48 h post-stress. F. Schematic representation of CeA punch dissection. Data are presented as mean ± SEM and analyzed using a one-way ANOVA. $ indicates p<0.05 versus Control rats, * indicates p<0.05 versus Non-Avoiders.