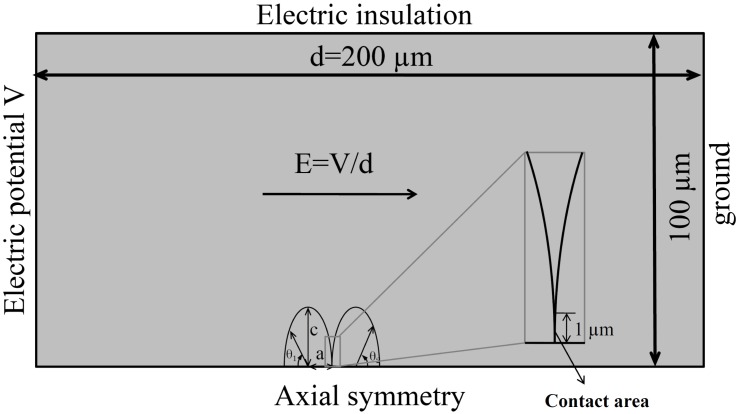
Fig 2. Model of two contact vesicles with axis ratios (k = 1/2) exposed to an electric field.
The axis ‘a’ is parallel to the direction of electric field (also the axis of symmetry). The magnitude of electric field (1.5 kV/cm) is determined as the potential difference between the two electrodes (electrode potential), divided by the electrode distance. The direction of the electric field is indicated with an arrow. Polar angle θ1 for the left vesicle arises along the clockwise direction, whereas polar angle θ2 for the right vesicle arises along the counterclockwise direction.