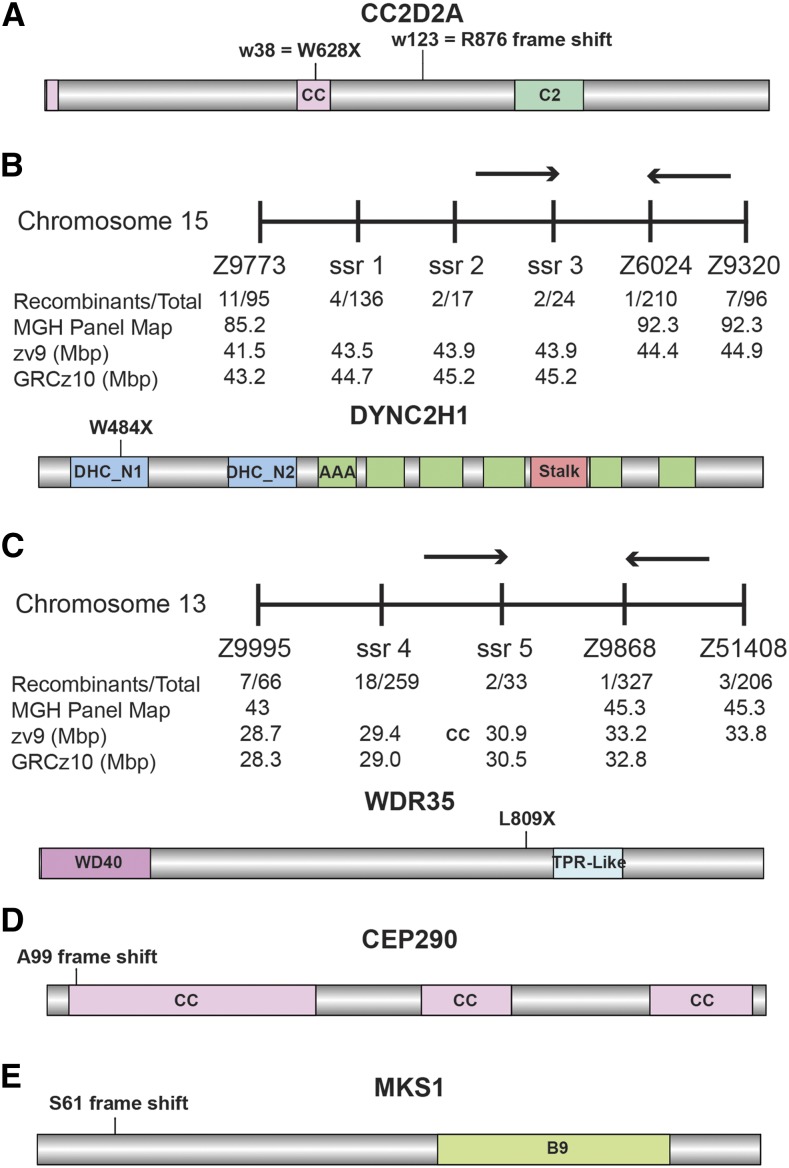
Figure 1.
Identification of mutations in cilia-associated genes that confer resistance to aminoglycoside-induced hair cell death. (A) Two mutations have been identified in the cc2d2a gene. One mutation (w38) (W628X; Owens et al. 2008) causes a premature stop codon in a coiled-coil (CC) domain. The other (w123) leads to the retention of the intron between exons 20 and 21 causing a frameshift. Both pink boxes are putative CC domains. (B) Top: neomycin-resistant mutant allele w46 mapped to a region of approximately 0.5 Mb on chromosome 15. The microsatellite markers used for mapping are shown, as well as the number of recombinant animals at each position. Bottom: sequencing of the dync2h1 gene contained in this region identified a G to A nucleic acid change in mutants at residue 1452, leading to a premature stop codon in the N-terminus of the protein (W484X). All green boxes represent AAA domains (ATPases Associated with diverse cellular Activities). (C) Top: neomycin-resistant mutant allele w150 mapped to a region of approximately 2.3 Mb on chromosome 13. The microsatellite markers used for mapping are shown, as well as the number of recombinant animals at each position. Bottom: sequencing of the wdr35 gene contained in this region identified a T to A nucleic acid change in mutants at residue 2426, leading to a premature stop codon just upstream of the tetratricopeptide repeat TPR-Like domain (L809X). (D and E) Frameshift mutations were generated in the N-terminus of both Cep290 (D) and Mks1 (E) using genome editing techniques. The cep290 mutation was a 2 bp deletion, resulting in a frameshift and truncated coding sequence after A99, whereas the mks1 mutation was a 25 bp insertion causing a frameshift and truncated coding sequence after S61. Due to the large range of sizes, the individual protein images are not to the same scale. DHC, dynein heavy chain domain.