Figure 3. The Rev C-C Interface, related to Fig. S5–S6.
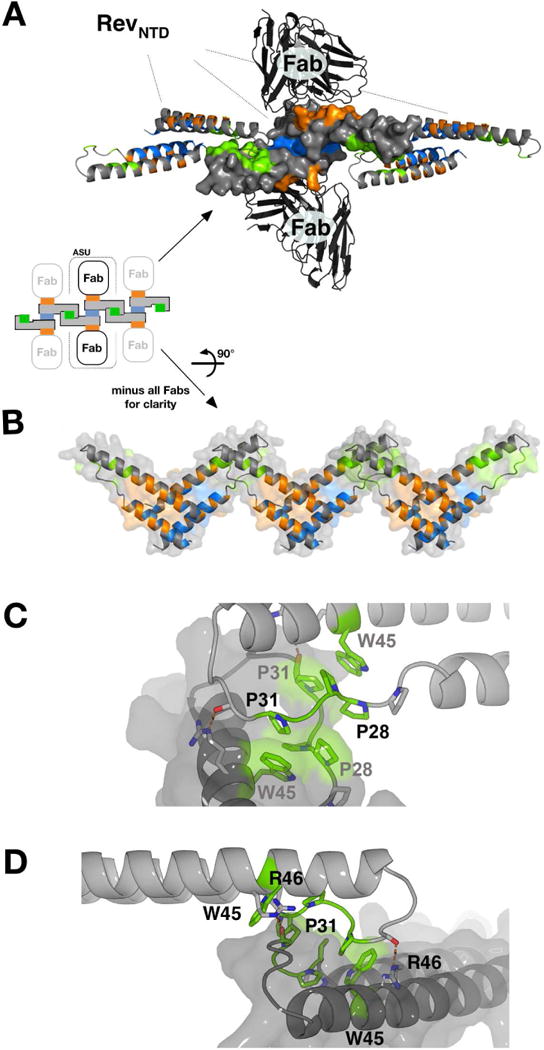
(A) Shown is the scFv-Rev P21 structure (PDB: 5DHV), with a Rev dimer at center (surface representation), formed through A-A interface (blue) and bound to two scFv molecules via B oligomerization surfaces (orange). The Rev dimer contacts two adjacent Rev dimers (ribbon representation) laterally via the C-C interface (green). Crystal packing of scFv-Rev lattices exhibits C-C interface in three of four space groups observed (see Fig S1).
(B) Rev dimers in (A) rotated 90°. The C-C interface bridges adjacent Re v dimers formed through the A-A oligomerization interfaces.
(C) The poly-proline loop (between α1 and α2) and W45 comprise the major contacts of the C-C interface. P28, P29, and P31 are involved, but P27 is not). The rigid poly-proline loops hook into each other, supported by stacking interactions between W45 and P31. The interface is further stabilized by two hydrogen bonds between R46 and backbone carbonyl moieties of the apposed subunit.
(D) Same as (C) but viewed from a different angle.
