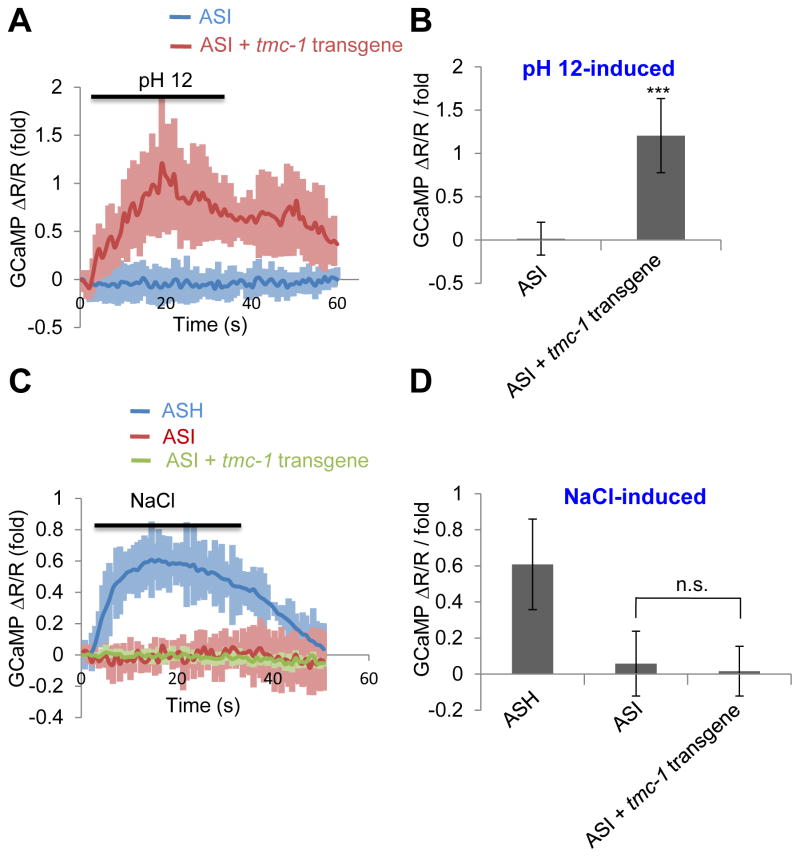
Figure 6. Ectopic expression of TMC-1 can confer alkaline sensitivity to alkali-insensitive cells.
(A–B) Ectopic expression of TMC-1 in ASI confers alkaline sensitivity to these neurons revealed by calcium imaging. ASH was labeled with GCaMP6 and DsRed (internal reference) which were co-expressed as a transgene using the sra-6 promoter. Bath solution (pH 12) was perfused towards the nose tip using a microfluidic system. As ASH neurons are alkali-sensitive and are also functionally connected to ASI neurons (Guo et al., 2015), imaging experiments were performed on worms with ASH ablated using a laser microbeam. tmc-1 cDNA was expressed in ASI under the sra-6 promoter. Shown in (A) are calcium imaging traces. Shadows along the traces denote error bars. Bar graph in (B) summarizes the data. n≥8. Error bars: SEM. ***p<0.0005 (t test).
(C–D) TMC-1 ectopically expressed in ASI does not promote NaCl sensitivity. Bath solution containing 500 mM NaCl was perfused towards the nose tip. As no notable response was detected in ASI in response to NaCl (500 mM), we imaged ASH of wild-type worms as a positive control, and observed NaCl-induced calcium transients. (C) Calcium imaging traces. (D) Bar graph. n≥8. Error bars: SEM. n.s.: not significant (t test).