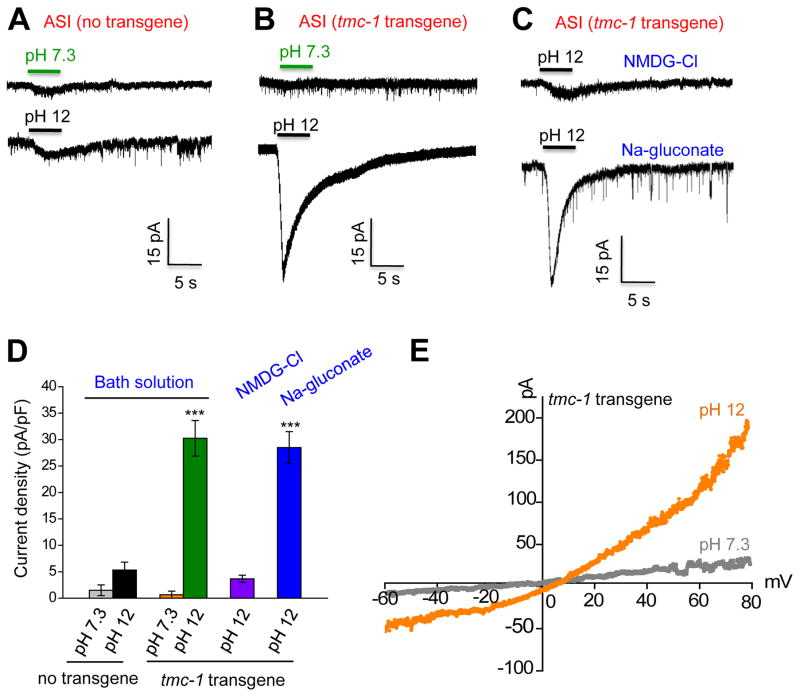
Figure 7. Ectopic expression of TMC-1 promotes alkali-activated currents.
(A–B) Ectopic expression of TMC-1 in ASI promotes alkali-activated currents. tmc-1 cDNA was expressed in ASI as a transgene with the sra-6 promoter. As ASH neurons express robust alkali-activated currents and are functionally connected to ASI (Guo et al., 2015), we mechanically removed ASH neurons prior to recording ASI. Little if any alkali-activated currents were detected in ASI neurons of worms carrying no tmc-1 transgene (A). By contrast, robust alkali-activated currents were detected in ASI carrying a tmc-1 transgene (B). Shown are sample traces. Voltage: −60 mV.
(C) Alkali-activated currents are primarily carried by cations. Little alkali-activated current was detected in bath solution containing NMDG-Cl. By contrast, a robust alkali-activated current was observed in bath solution containing Na-gluconate. Voltage: −60 mV.
(D) Bar graph summarizing the data in (A–C). n≥9. Error bars: SEM. ***p<0.0005 (ANOVA with Dunnett’s test).
(E) I–V relations of alkali-activated currents in ASI of worms carrying a tmc-1 transgene. A voltage ramp (−60 to +80 mV; 200 ms) was applied to ASI.