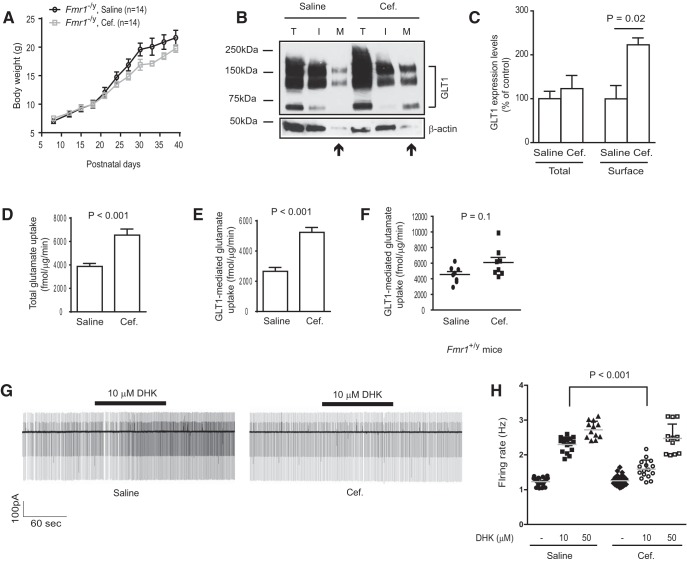
Figure 7.
Pharmacological upregulation of functional GLT1 expression attenuates enhanced neuronal excitability in cortex of Fmr1 KO mice. A, Body weight changes of saline- and Cef-injected Fmr1 KO mice during early postnatal development; n = 14 mice/group. B, A representative immunoblot of GLT1 protein levels in total (T), intracellular (I), and membrane (M) fractions prepared from saline- or Cef-injected Fmr1 KO cortical tissues. C, Quantification of total and surface GLT1 protein levels in cortex of saline- or Cef-injected Fmr1 KO mice; n = 3 mice/group. D, E, Total (D) and GLT1-mediated (E) glutamate uptake from saline- or Cef-injected Fmr1 KO cortical tissues; n = 7–10 mice/group. F, GLT1-mediated functional glutamate uptake from saline- and Cef-injected WT (Fmr1+/y) cortical tissues; n = 8 mice/group. G, A representative trace of neuronal firing recordings in layer 5 somatosensory neocortical neurons in saline- or Cef-injected Fmr1 KO cortical slices before and during the bath application of GLT1 inhibitor DHK (10 μm). H, Quantitative summary of neuronal firing rates in saline- or Cef-injected Fmr1 KO cortical slices with 10 or 50 μm DHK; n = 12–28 neurons from 7 to 10 mice per group. The p values were determined using the Student's t test, one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey's test, and two-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni's test.