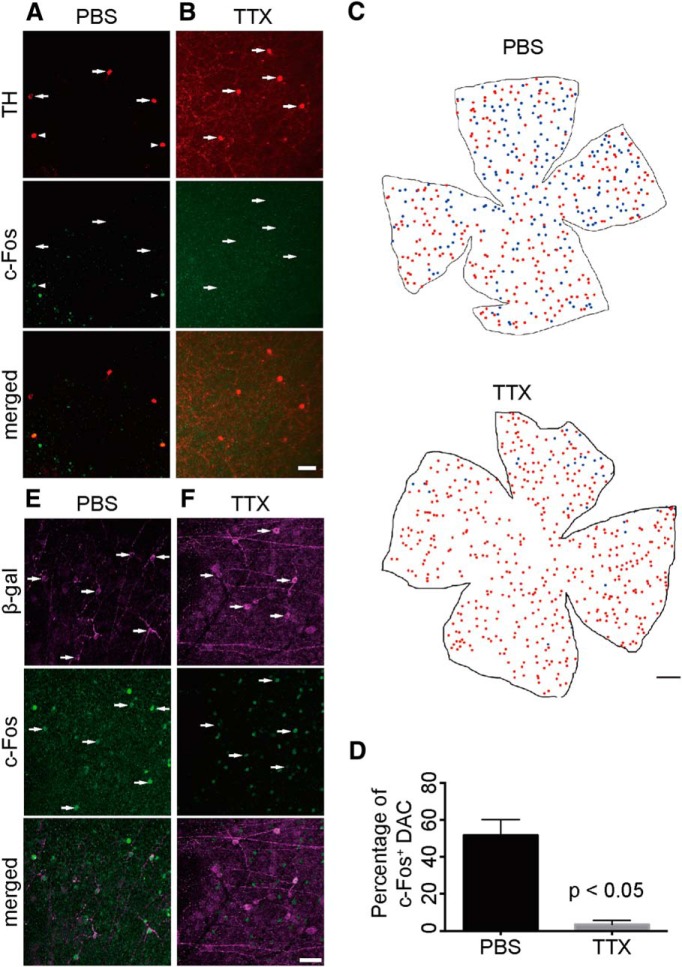
Figure 3.
TTX ablates melanopsin-mediated activity of DACs in vivo. A, Whole-mount retina with TH, β-galactosidase, and c-Fos triple immunofluorescence staining from a rod and cone transducin double knock-out and Opn4-tau-LacZ background mouse (Opn4tau−LacZ/+ Gnat1−/− Gnat2−/−). At the IPL, some TH+ DACs (indicated by white arrowheads) were colabeled with c-Fos (green) after 90 min of white light (400 lux) exposure after intraocular injection of PBS. B, Intraocular injection of TTX before light exposure blocked c-Fos expression in DACs (indicated by white arrows). C, Illustration depicting the distribution of DACs in the whole-mount retina after light exposure from a PBS-injected retina (top) and a TTX-injected retina (bottom). Red dots indicate c-Fos-negative DACs, blue dots indicate c-Fos-positive DACs. In the TTX-injected retina, almost all DACs were c-Fos negative. D, Quantification of c-Fos-positive DACs after 90 min white light exposure. The percentage of c-Fos-positive DACs in the TTX injection group (n = 3) was near zero and was significantly lower than in the PBS injection group (n = 3). E, F, Most M1 ipRGCs, labeled by β-galactosidase antibody (magenta), are c-Fos (green) positive after 90 min of light exposure (indicated by white arrows) in both the PBS control group (E) and the TTX intraocular injection group (F). Scale bars: A, B, 50 μm; C, 1000 μm; E, F, 50 μm.