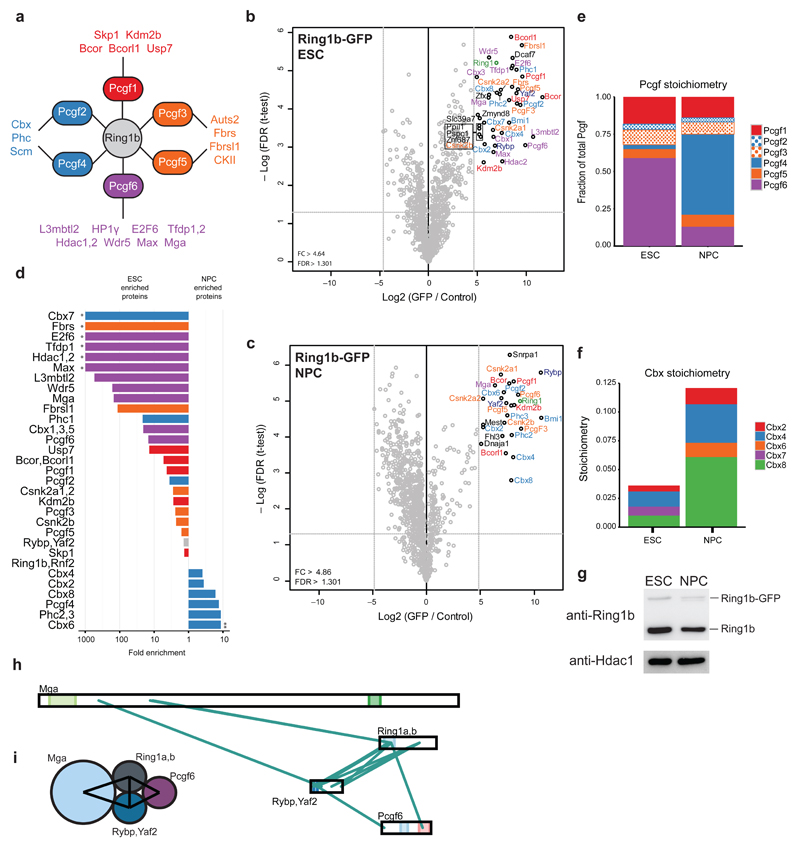
Figure 4. PRC1 interactors and architecture during stem cell differentiation.
(a) Schematic of the PRC1 complex showing the core catalytic subunit Ring1b as well as all 6 Pcgf proteins and a summary of their known interactors. (b,c) Volcano plot from label-free GFP pulldowns on Ring1b-GFP ESC (b) or NPC (c) nuclear extracts graphed as in Fig. 1b. Snrpa1 and Fhl3 are known GFP contaminants. (d) Logarithmic plot of the ratio of ESC enrichment (left) or NPC enrichment (right) for Ring1b-GFP interacting proteins. (*) only detected in ESC pulldown (**) only detected in NPC pulldown (e) Pcgf protein stoichiometry values in ESCs and NPCs. Results are presented as the fraction of total Pcgf bound to the complex. (f) Cbx protein stoichiometry values from ESCs and NPCs. (g) Western blot of GFP-tagged and endogenous Ring1b on nuclear extracts from ESCs and NPCs with Hdac1 used as a loading control. Uncropped blots appear in Supplementary Data Set 1. (h) Visualization of cross-links identified from single affinity purified Ring1b-GFP from ESCs. Ambiguous cross-links between paralogous subunits (Ring1a and Ring1b, Rybp and Yaf2) are combined in this visualization. (i) Summary of PRC1 architecture in ESCs based on cross-links shown in (h).