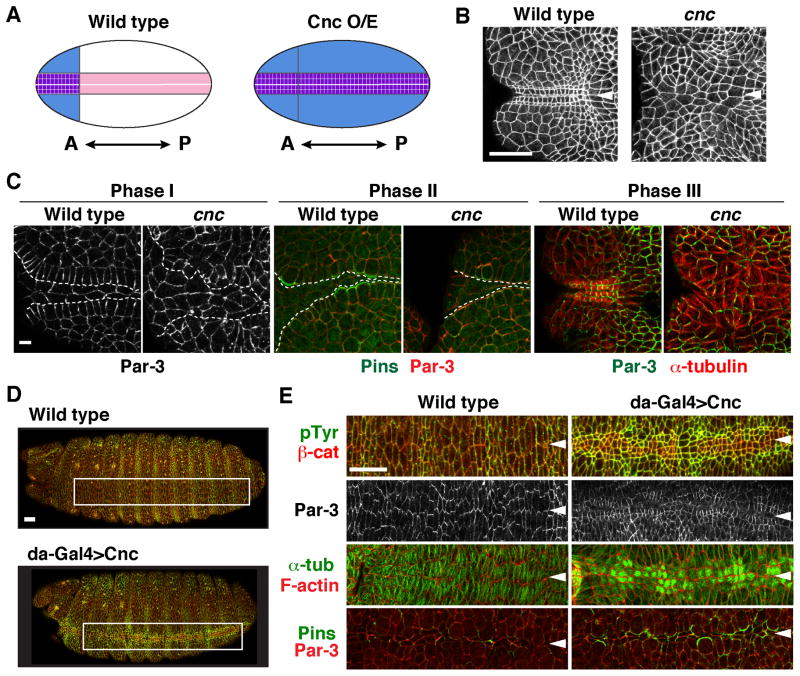
Figure 4. The Cap ‘n’ collar transcription factor is necessary and instructive for square grid formation.
(A) Schematic of results. Cnc (blue) is expressed in the anterior ventral embryo during square grid formation (left). The wild-type grid forms within this domain. Ubiquitous Cnc expression (Cnc O/E) induces a square grid (purple) along the entire ventral midline (right). (B) The square grid fails to form in cnc mutants (stage 13). (C) The cnc mutants displayed defects in multiple processes required for square grid formation, including cell alignment in Phase I (left), Pins asymmetry in Phase II (middle), and apicobasal microtubule reorganization in Phase III (right). Dashed lines, boundaries between midline cells and the square grid. (D) Ubiquitous Cnc expression with the da-Gal4 driver induced square cells along the ventral midline (stage 14, boxed regions shown at higher magnification in E). (E) These cells displayed several features of the wild-type grid, including square cell packing (stage 14) (top panels), Par-3 localization perpendicular to the midline (stage 13), microtubule reorganization (stage 13), and Pins asymmetry (stage 11). Arrowheads, ventral midline. Bars, 5 μm in C, 20 μm in B, D, and E.