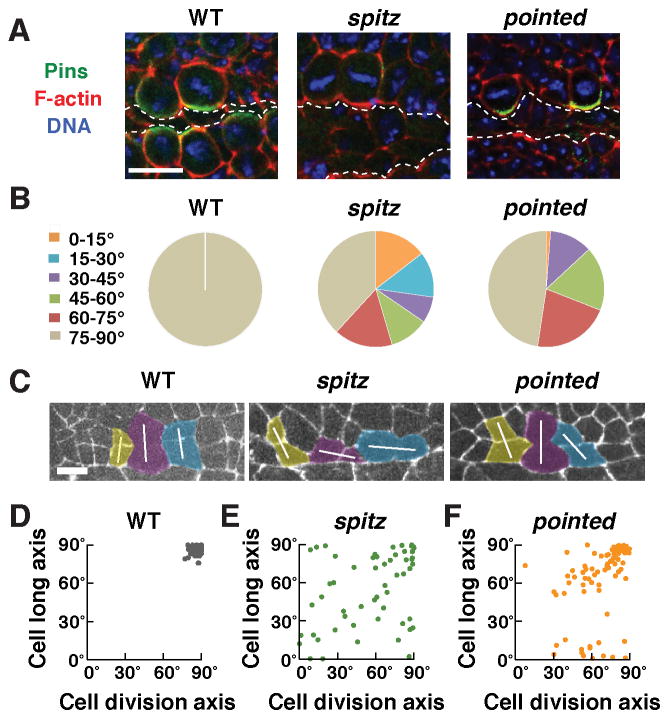
Figure 6. The EGF receptor ligand Spitz is required for Pins asymmetry and oriented cell division.
(A) Pins asymmetry was absent in spitz mutants (0/19 cells in 6 embryos), but occurred normally in pointed mutants (25/27 cells in 7 embryos), similar to wild type (33/35 cells in 5 embryos). (B) Quantification of the cell division axis (0° is parallel to the ventral midline). All wild-type cells divided at 75–90° relative to the midline. Cell divisions were frequently misoriented in spitz (62%) and pointed (52%) mutants (55–84 cells in 3–4 embryos/genotype). (C) Stills from time-lapse movies of wild-type, spitz, and pointed mutant embryos expressing β-catenin:GFP. White lines indicate the division axis. (D) The cell division axis correlates with the long axis of the cell in wild type. (E,F) Cells divided at a wider range of orientations and the cell division axis was not well correlated with the cell long axis in spitz (linear correlation coefficient R2 = 0.14) and pointed (R2 = 0.18) mutants. The orientation of the cell long axis in spitz mutants (55°±4°) was significantly different from wild type (86°±0.4°), but was less strongly affected in pointed mutants (64°±3°) (p = 0.06, spitz vs. pointed) (unpaired t test). Bars, 10 μm in A, 5 μm in C.