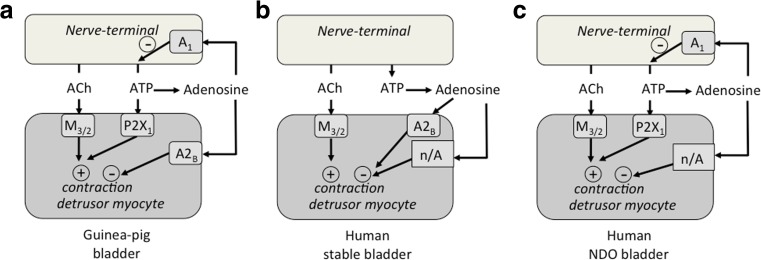
Fig 7.
A model of the effects of adenosine on nerve-endings and smooth muscle to modulate contractile function in human and guinea-pig detrusor. a: Guinea-pig bladder. Acetylcholine (ACh) and ATP bind to M3 and P2X1 receptors respectively. Adenosine, derived from ATP breakdown in the nerve-muscle junction, binds to A2B (detrusor) and A1 (nerve endings) receptors. b: Human stable bladder. ACh binds to M3 receptors; ATP is completely broken down in the nerve-muscle junction. Adenosine has an effect via non-A receptors (n/A) on detrusor. c: Human NDO bladder. ACh binds to M3 receptors; ATP is incompletely broken down and activates detrusor via P2X1 receptors. Adenosine acts on detrusor via non-A receptors and binds to nerve-terminal A1 receptors. + activation, − inhibition