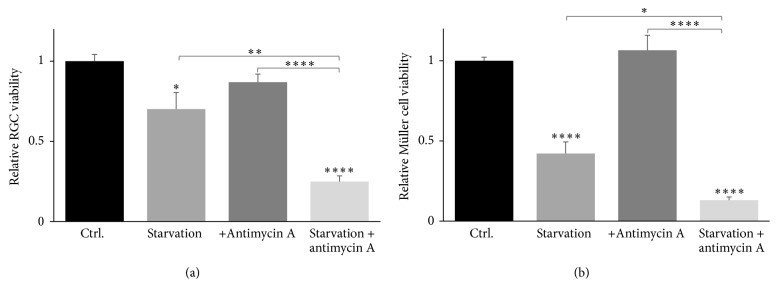
Figure 3.
Cell viability of primary RGCs and primary Müller cells in response to starvation and mitochondrial inhibition. By means of LDH assays, starvation for 24 hours was shown to decrease RGC survival significantly to 70% ((a); ∗ P < 0.05, ∗∗ P < 0.01) compared to control. Likewise, starvation of Müller cells significantly decreased their survival to 42% of control ((b); ∗∗∗∗ P < 0.0001). Mitochondrial inhibition by exposure to 10 μM antimycin A did not affect RGC and Müller cell survival ((a) and (b), resp.), whereas simultaneous starvation and exposure to antimycin A significantly reduced RGC and Müller cell survival to 25% and 13%, respectively ((a) and (b); ∗∗∗∗ P < 0.0001). Bars represent mean values ± SEM of 5–8 experiments. Differences in survival were tested using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test.