Fig. 1.
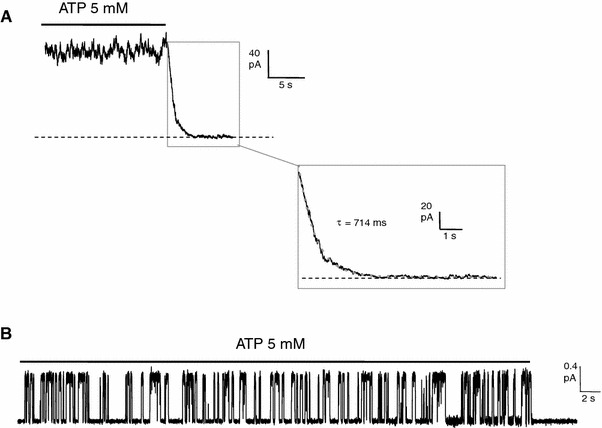
Macroscopic and microscopic currents of wild-type (WT)-CFTR. a Macroscopic WT-CFTR current after a rapid removal of 5 mM ATP. The current relaxation was fitted with a function: 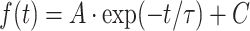 , where τ and A is time constant and amplitude of the current relaxation and C is a constant (gray dashed line in inset). Note that the constant C approximates a very small and slow component possibly underlied by long-lasting opened WT-CFTR channels (see Fig. 5). b A representative current trace of WT-CFTR channel showing immediate closing upon a rapid removal of ATP
, where τ and A is time constant and amplitude of the current relaxation and C is a constant (gray dashed line in inset). Note that the constant C approximates a very small and slow component possibly underlied by long-lasting opened WT-CFTR channels (see Fig. 5). b A representative current trace of WT-CFTR channel showing immediate closing upon a rapid removal of ATP
