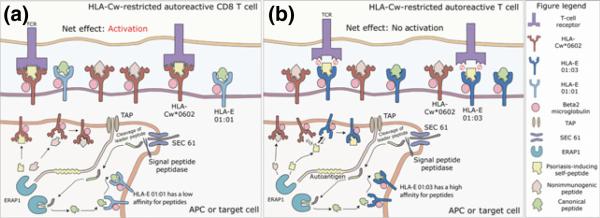
Figure 2. Determinant capture as an alternative model to explain the link between HLA-E and psoriasis.
Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) functions to process peptides within the endoplamic reticulum, which are then presented by HLA molecules on antigen presenting cells or target cells to autoreactive CD8+ T-cells.
A.) HLA-Cw*0602 Restricted Autoreactive CD8+ T-cells. HLA-E 01:01 has a lower affinity for peptides compared to HLA-Cw*0602. It presents mainly canonical peptides derived from the leader sequence of classical HLA class one molecules. Psoriasis-inducing self peptides presented by HLA-Cw*0602 on the surface of an APC or target cells are recognized by autoreactive T-cells, resulting in activation of pathogenic CD8+ T-cells, predisposing to psoriasis.
B.) HLA-E 01:03 captures the psoriasis-inducing self-peptide from HLA-C. The increased peptide-binding affinity of HLA-E 01:03 allows it to outcompete HLA-Cw*0602 for binding to the ERAP1-processed psoriasis-inducing self-peptide. The HLA-E 01:03-presented self-peptide is not recognized by autoreactive CD8+ T cells due to incompatible binding sites between the TCR and HLA-E MHC molecule. As a result, activation of the autoreactive CD8+ T-cell is prevented. HLA-E 01:03 is protective against psoriasis in HLA-Cw*0602 positive patients.