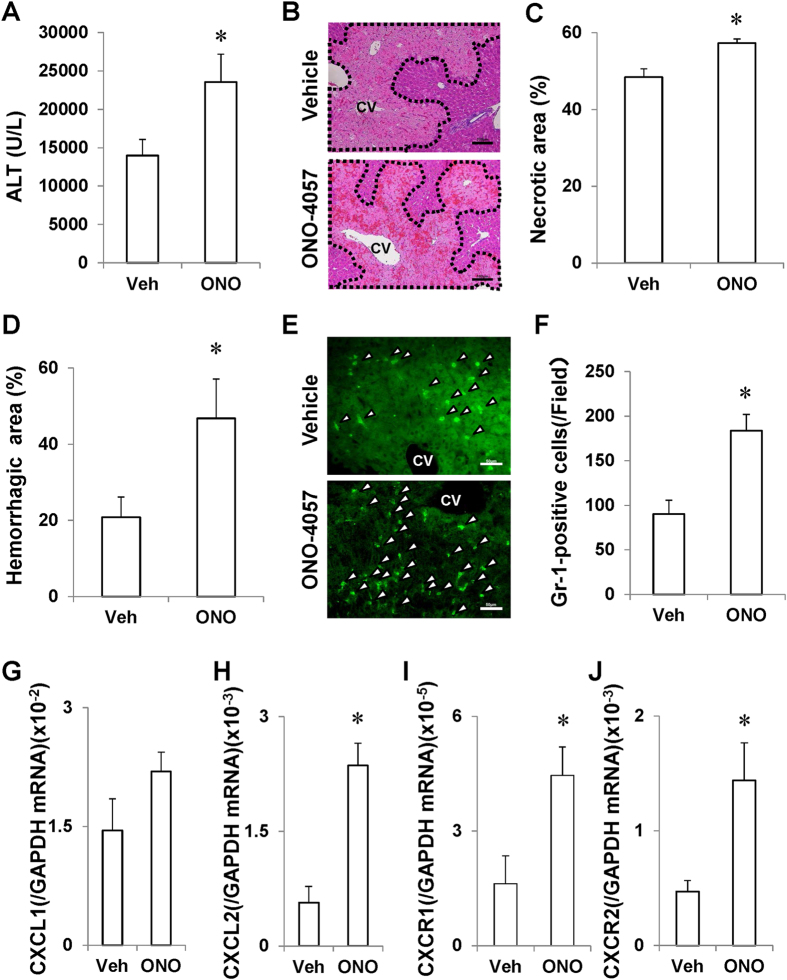
Figure 3. Pharmacological inhibition of BLT1 with ONO-4057 exacerbates APAP-induced liver injury in WT mice.
(A–C) Treatment of WT mice with a BLT1 antagonist, ONO-4057, aggravated APAP-induced liver injury at 24 h post-treatment, as evidenced by an increased ALT level (A), a larger necrotic area (B,C) and a larger haemorrhagic area (D) in comparison with WT mice treated with vehicle (Veh). (B) Typical images of H&E staining of livers in vehicle-treated mice (upper panel) and ONO-0457-treated mice (lower panel) at 24 h after APAP injection. Necrotic area is delineated with the black dashed line. CV, central vein. Bars = 100 μm. ONO, ONO-4057. Data are expressed as the means ± SEM of 5–6 mice per group. *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle (Veh)-treated WT mice. (E) Typical images of immunostaining with an anti-Gr-1 antibody in livers of vehicle-treated mice (upper panel) and ONO-0457-treated mice (lower panel) at 24 h after APAP injection. Arrow heads indicate Gr-1-positive cells. CV, central vein. Bars = 50 μm. (F,G) Treatment of WT mice with ONO-0457 increased the recruitment of Gr-1-positive cells into the liver (E,F) and increased the mRNA levels of chemokines and their receptors including CXCL2 (H), CXCR1 (I) and CXCR2 (J), but not CXCL1 (G), at 24 h after APAP administration. Data are expressed as the means ± SEM of 5–6 mice per group. *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle (Veh)-treated WT mice. ONO, ONO-4057.