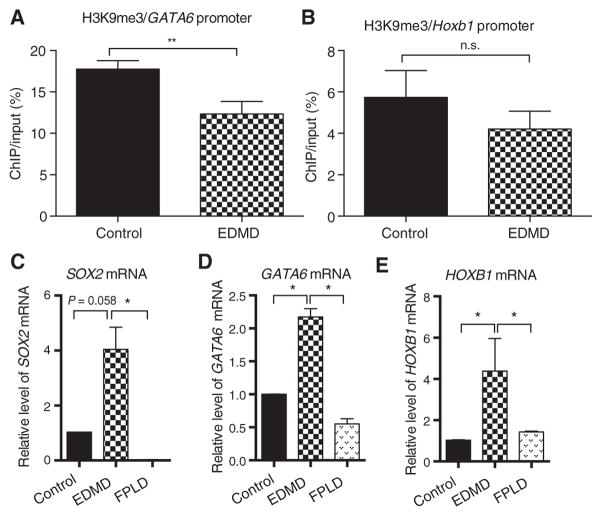
Fig. 6. Various lamin A/C mutations that cause either EDMD or FPLD give rise to differential regulation of Sox2 pathways.
Dermal fibroblasts from an EDMD patient carrying a lamin A/C p.H222P dominant mutation, an FPLD p.R482W lamin A/C mutation, and a control volunteer were converted to myogenic lineages, differentiated, and studied for Sox2 pathway gene regulation. (A and B) ChIP for the H3K9me3 heterochromatin mark showed mutation-specific loss of heterochromatin in EDMD for both Gata6 and Hoxb1. (C to E) Steady-state mRNA levels for the (C) Sox2, (D) Gata6, and (E) Hoxb1 genes in differentiated control, EDMD, and FPLD myogenic cells measured by qRT-PCR. For experimental versus control, *P = 0.05 and **P = 0.01. Error bars indicate ±SEM.