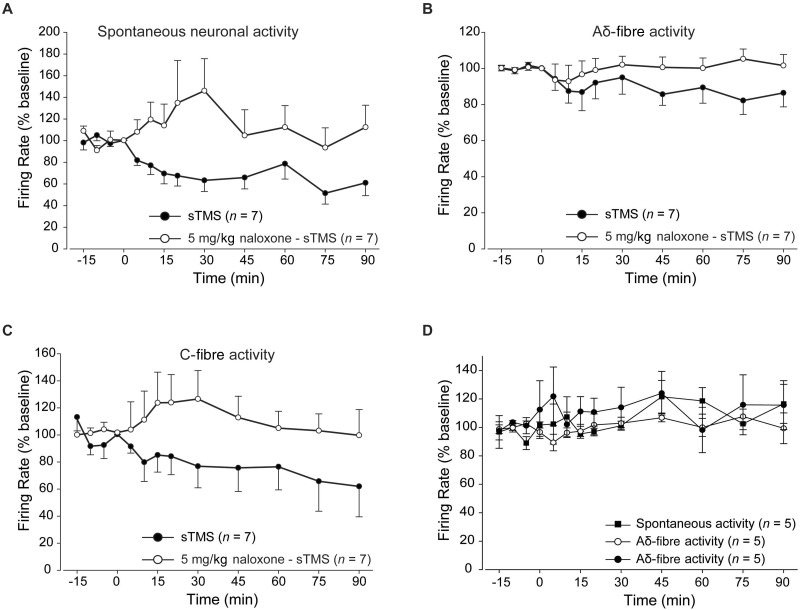
Figure 5.
The impact of opiodergic mechanisms on thalamocortical TMS responses. Pretreatment with naloxone (5 mg/kg; intravenous bolus) 5 min pre-single pulse TMS application significantly blocked the inhibitory effects of single pulse TMS over the spontaneous and evoked firing of third order neurons. Graphs demonstrate the comparison between the single pulse TMS group with and without naloxone pre-treatment over the spontaneous neuronal activity ( A ) and trigeminovascular evoked activity in response to Aδ- ( B ) and C-fibre activation ( C ). ( D ) Naloxone administered alone, in the absence of single pulse TMS, induced no significant changes over spontaneous or evoked trigeminovascular activity in response to Aδ- and C-fibre activation.