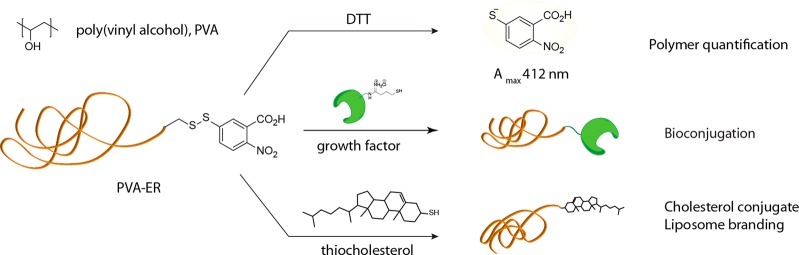
Figure 1.
Chemical formula of PVA (top) and schematic illustration of chemical reactions of PVA via terminal groups activated toward thiol–disulfide exchange. Cleavage of the terminal disulfide (be it in solution or within the gel phase) liberates a chromophore—allowing to quantify the polymer chains via a solution-based UV–vis readout; reaction with thiol-modified growth factors creates hydrogel matrices for localized stimulation of proliferation of adhering cells; conjugation to cholesterol is used toward anchoring PVA chains into liposomes and “branding” the latter within the structure of PVA hydrogels—for delivery of hydrophobic drugs.