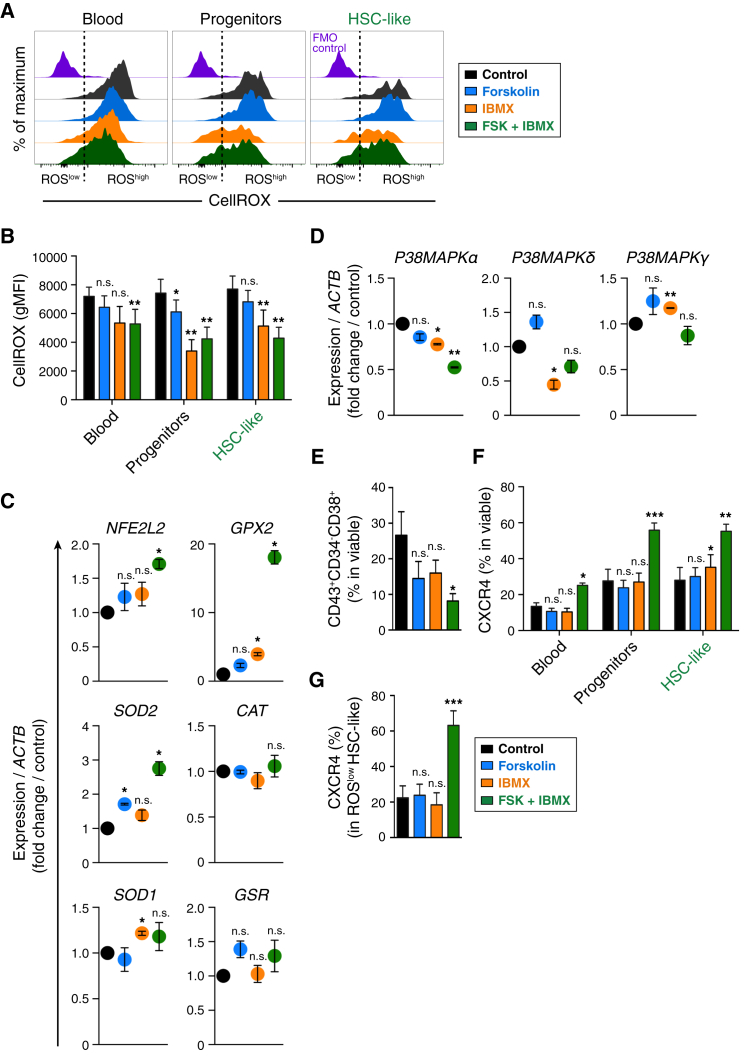
Figure 3.
cAMP Induction Reduces Oxidative Stress and Induces CXCR4 in hPSC-Derived Hematopoietic Cells
(A) Flow cytometry analysis for detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in differentiated hPSC-to-hematopoietic cells at day 14 of differentiation. Representative flow cytometry plots (biexponential x axis) show ROS levels in the hematopoietic surface phenotypes. FMO control, fluorescence-minus-one (staining control).
(B) Quantification of geometric mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) of CellROX dye as indicated in (A). Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using the t test. Significance compared with the control setting: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; n.s., not significant.
(C and D) qRT-PCR expression analysis of the indicated redox-state-regulating genes (C) and p38MAPK-related genes (D) in PSC-derived hematopoietic cells. Relative expression of each gene to housekeeping gene ACTB (β-ACTIN) was calculated, and mean fold change respective to control condition (set at 1) is shown. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using the t test. Significance compared with the control setting: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01; n.s., not significant.
(E) Analysis of mature hematopoietic progenitors (CD43+CD34−CD38+) after cAMP induction (day 14). Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using the t test. Significance compared with the control setting: ∗p < 0.05; n.s., not significant.
(F) Expression of CXCR4 across indicated hematopoietic surface phenotypes. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using the t test. Significance compared with the control setting: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001; n.s., not significant.
(G) Expression of CXCR4 in HSC-like surface phenotype (ROSlow fraction). Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using the t test. Significance compared with the control setting: ∗∗∗p < 0.001, n.s., not significant.
See also Figure S3.