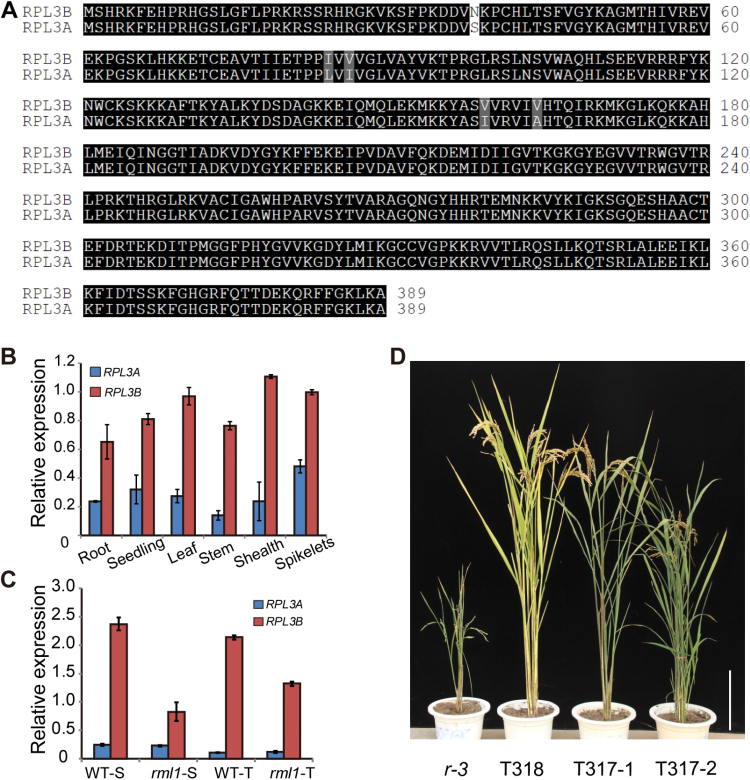
Fig. 6.
Function comparisons between RPL3A and RPL3B. (A) Clustal alignment of the two rice RPL3 amino acid sequences (RPL3A and RPL3B). Identical and similar residues are shaded black and grey, respectively; the difference is highlighted with no shading. (B) Expression of RPL3B was higher than RPL3A in all tissues analysed. (C) Results from real-time PCR assay showing that expression of the RPL3B gene is reduced in the rml1 mutant, whereas that of RPL3A is unchanged relative to the wild-type. (D) Genetic complementation of rml1 with pRML1:gRML1 (T318) and pRML1:cRPL3A (T317) constructs. Ubiquitin (UBQ) was used as an internal control in real-time PCR. Error bars indicate ±SD (n 3). Abbreviations: S, seedling stage; T, tilling stage. Scale bar in (D) is 20cm.