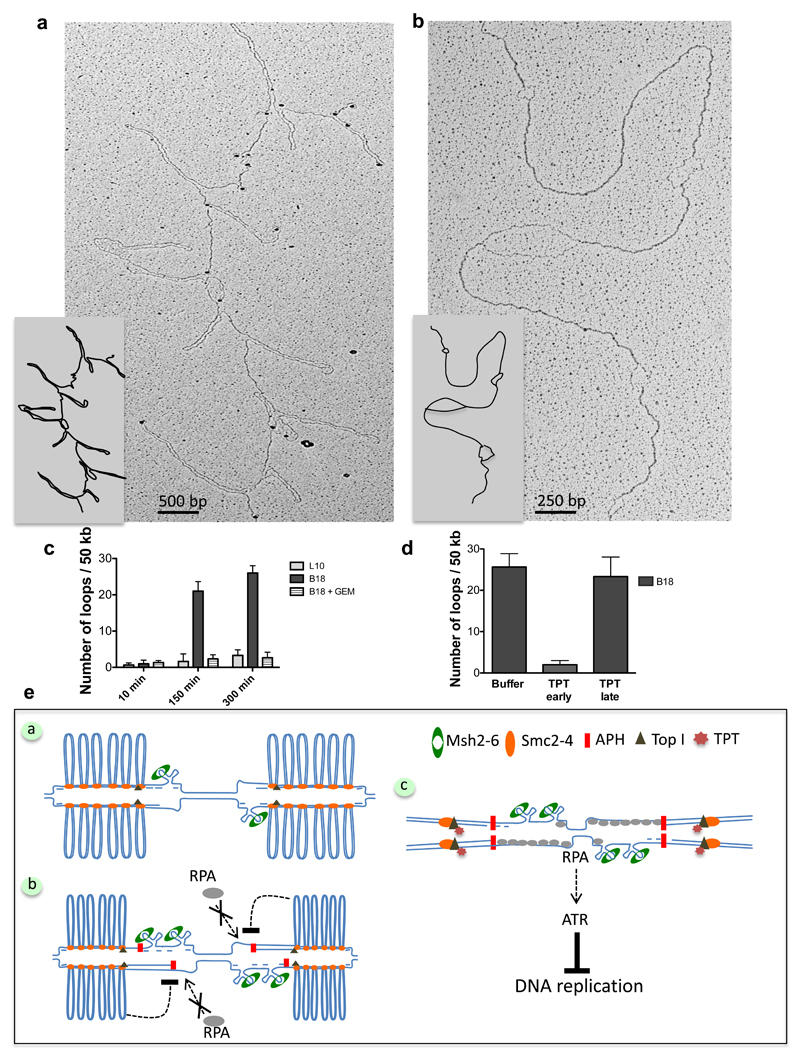
Figure 5. Centromeric BACs generate stable double stranded DNA loops during DNA replication.
(a) EM of centromeric B18 chromatin isolated after partial proteinase K digestion (See Methods). (b) EM analysis of samples isolated as in (a) and subjected to complete protein digestion. (c) Graph showing the frequency of DNA loops in L10 or B18 DNA incubated in extracts that were untreated or treated with geminin (Gem) for the indicated times. Experiments were repeated three times scoring the equivalent of about one mega base of DNA in total. Error bars represent ± sd of the mean. n=3 experiments; p<0.001 when comparing L10, B18 and B18 + Gem mean values for the indicated times; One-way Anova. (d) Frequency of loops on B18 DNA incubated in extracts supplemented with buffer or treated with TPT at the start of reaction (TPT early) or after its completion at 300 minutes (TPT late) and collected one hour later. Experiments were repeated three times scoring the equivalent of about one mega base of total DNA. Error bars represent ± sd of the mean. n=3 experiments; p<0.001 when comparing B18 mean values for all treatments; One-way Anova. (e) Model illustrating arrangement and response to replication stress of centromeric chromatin, which is organized in loops of dsDNA formed in the presence of Condensins (SMC2-4) and active Topoisomerase I (Top I). Loops accumulate most likely behind replication forks. Individual centromeric repeats might form hairpins or other secondary structures on unwound ssDNA at replication forks, attracting MMR proteins, which might be required to resolve them (Panel a). This topological arrangement limits the formation of extensive ssDNA regions and RPA hyper-loading onto chromatin triggered by the uncoupling of helicase and polymerase induced by aphidicolin (APH) or other fork stalling events. Inhibition of RPA binding to chromatin prevents activation of ATR. ssDNA generated during fork uncoupling folds into several hairpins, leading to MMR proteins accumulation (Panel b). Interference with contromeric DNA topology by Toposimerase I inhibitor (TPT) restores RPA loading and ATR activity, which inhibits centromeric DNA replication (Panel c), suggesting that topology dependent suppression of ATR normally facilitates replication of hard-to-replicate repetitive DNA sequences present at the centromere.