Figure 5.
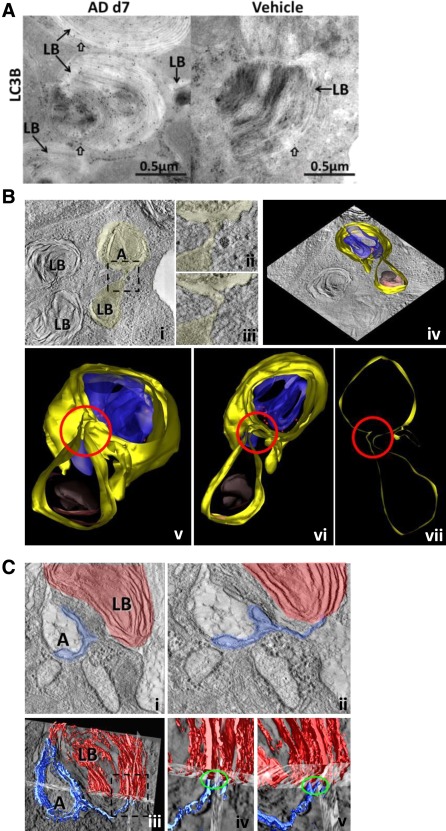
AD induces fusion between autophagosome and lamellar bodies in AECII. (A) Representative images from immunogold labelling for LC3B on lung sections of AD (day 7) and vehicle treated mice. Arrows indicate preferential binding of LC3B to lamellar bodies (LB) in AECII. Block arrows indicate LC3B‐bound gold particles in close proximity to the limiting membrane of LB of AECII in AD and vehicle‐treated mice. Scale bar=0.5 µm. (B) Single slice of EM tomogram showing a direct link between autophagosomes (A) and lamellar bodies (LB) via membranes (i); the boxed area is shown at higher magnification in (ii, iii). Different slices of the tomogram showing that the limiting membrane of the lamellar body and the autophagosome share the same membrane are shown adjacent to these images (iv). In the lower panel (v‐vii), different rotation views of the model of the connection between LB and the autophagosome are shown: the junction is highlighted by a red circle. Colour code: yellow, limiting membranes; blue, membranous content of the autophagosome; red, ribosomes; grey, core of the lamellar body; brown, lipid lamellae. (C) A second example obtained by means of EM tomography showing a direct link between autophagosomes (A) and lamellar bodies (LB) via membranes (i). The membranes of the LB also protrude and form a double membrane layer of an autophagosome which separates a compartment of low density within the autophagosome from the cytosol (ii). The lower row (iii‐v) represents a 3D reconstruction of the membranes of a LB (red) and the membranes of the autophagosome (blue).
