Figure 2.
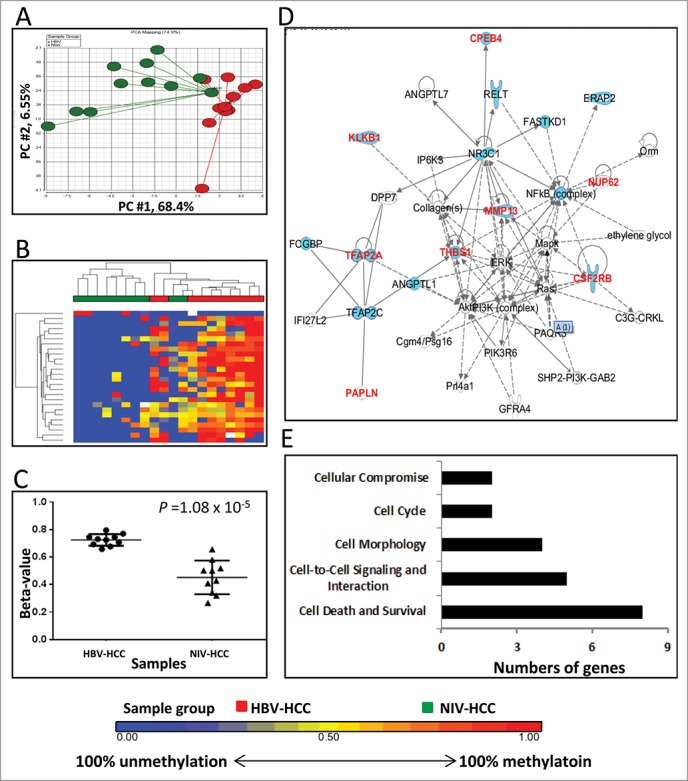
Differentially methylated CpGs between HBV-HCC vs. NIV-HCC. (A) Principal component analysis of the methylation data was plotted using the first 2 principal components (PC1 = 68.4% and PC2 = 6.55%). Each dot represents a sample (red for HBV-HCC and green for NIV-HCC). (B) Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of β-values for differentially methylated loci. Red and green blocks on the top of the maps represent HBV-HCC (n = 10) and NIV-HCC (n = 10), respectively. (C) Mean methylation level for all 7 differentially-methylated loci among HBV-HCC (left) and NIV-HCC (right). (D) The top IPA network involving differentially methylated genes. Red and blue genes indicate differentially methylated genes and the connected cancer related genes, respectively. (E) The top associated cellular functions with numbers of differentially-methylated genes.
